10Inventions That Were Developed Earlier Than You Think
Similar to flying cars, there are many advanced technological inventions that people have long expected to turn into reality, which did not happen, but there are many inventions that were developed in premature times, some of which became very popular and led directly to modern technologies that we use today Some of them were forgotten and lost in the past, until the world regained the need for their ideas and revived them centuries after their first appearance.
In this article on your income knowing website, we will provide you with a list of ten premature inventions that you did not know were invented long ago:
1. Armored vehicles:
In the fifteenth century in Italy, the famous Italian scientist “ Leonardo da Vinci ” drew designs for an armored fighting vehicle, which can be considered the first predecessor of armored cars and tanks today, as it had a conical shape inspired by the tortoise shell, and a number of lightweight cannons that surrounded its structure.

da Vinci armored vehicle
To move, this armored vehicle relied on four strong men to rotate two large cranks, and in this design the gears were so poorly distributed that the wagon could not work, and some believe that this was a deliberate mistake on the part of Da Vinci in the event that his designs were stolen.
In 2010, a team of engineers corrected errors in the designs and reconstructed a copy of this vehicle, but it was too large to move in rough terrain, and it is also believed that da Vinci designed this weapon in order to intimidate the enemy and not for Make it an effective fighting weapon. ( Source 1 , Resource 2 , Resource 3 )
2. Analog computers:
The Antikythera mechanical mechanism is a device dating back to the second century BC, and it is a complex mechanical mechanism created by connecting thirty gears, which was used for keeping the calendar and for astronomical purposes as well.

Antikythera mechanism
This mechanism was able to predict some astronomical positions during certain dates, and by rotating a hand crank, the date would change and the machine would start synchronously calculating the position of the moon, the sun, lunar eclipses, and chronological cycles. It is also believed that it could even predict the positions of the planets.
The technology behind this mechanism disappeared until astronomical clocks were invented and developed in the fourteenth century in Europe. The Antikythera mechanism was discovered in the year 1900 in the wreck of an ancient Greek ship.
Museum staff inspected the device for two years, and at first glance it looked like corroded scrap of rusty bronze and wood. ( source )
3. Automatic Vending Machines:
The credit for many premature and ancient inventions goes back to Hero of Alexandria who lived from ten to seventy AD. The world's first automatic vending machine is considered one of his most famous inventions, which worked by using coins in exchange for pumping and releasing a certain amount of holy water.

The first automatic vending machine
This invention helped temples prevent devotees from taking more than their share of this “holy” water, and the mechanism of the internal machine was simple, as a coin was inserted into the slot designated for it in the machine, which fell on top of a lever, the weight of the coin pushes the lever Downward opening a valve through which holy water descends, and when the lever is sufficiently tilted, the coin slides into a box and the valve closes.
Vending machine technology did not last long, as it went into oblivion until the 1880s, when the idea was revived and developed and the first commercial vending machine made for selling postcards appeared. ( source 1 , source 2 )
4. Automatic doors:
One of the many inventions that is credited to Hero of Alexandria is the idea of automatic doors, or automatic doors. hidden, then the doors appear to have opened by themselves.

automatic doors
The principle of operation of this technique included the use of heat from the fire in order to expand the air inside a container, and this heated air would then create a kind of pressure, which in turn would pump water into a group of buckets, and the buckets here play the role of weights that tighten the ropes that It in turn spins the spindles, eventually opening the doors, and once the doors are opened the mechanism blows compressed air through the horns as a dramatic conclusion to the show.
When the fire is extinguished and the altar cools, the mechanism reverses its working principle, automatically emptying the buckets of water, allowing the weights to close the gates.
Although the debate over whether Hero actually built his designs, her ideas were truly premature, and it wasn't until 1931 that the first model of automatic doors was invented, patented, and used. ( source 1 , source 2 )
5. Programmed robots:
This may seem a bit exaggerated, but the first programmed robot was also designed by Hero of Alexandria, which consisted of a wheeled cart moved by descending weights, and by wrapping a tape around the wheel hub, the cart could be programmed to follow a specific path.
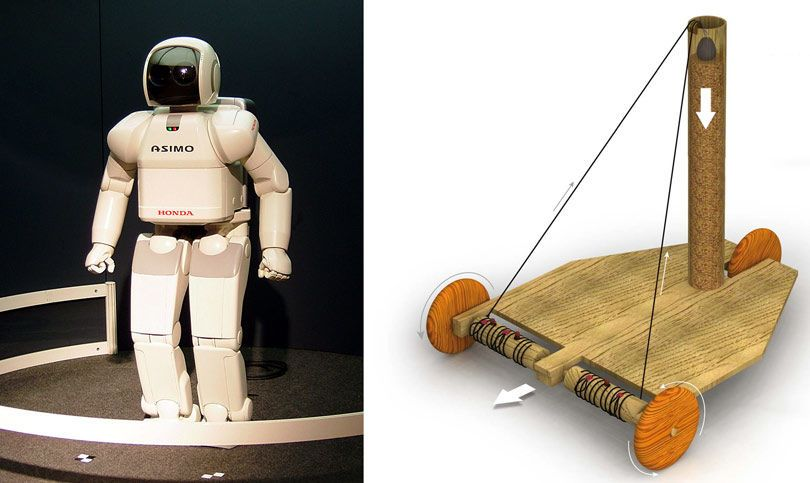
programmed robots
The descending weights were attached to a strap or string wound around the wheel hub, and there were pegs on this hub that allowed the string to turn in different ways allowing control of the cart's rotation or progress, and vice versa.
This robotic chariot has been used in theaters to contribute to the performance of some programmed and automated performances on stage, and Hiro is believed to have once created a mechanical play that featured programmed actors dancing and pouring wine. ( Source 1 , Resource 2 , Resource 3 )
6. Heat Ray Weapons:
The ancient Greek history recorded that Archimedes invented a heat ray that he used to burn enemy ships during the siege of “Syracuse” in the year 214 to 212 BC. This invention included the use of large mirrors arranged and arranged on the beaches to focus the sun’s rays on one point.
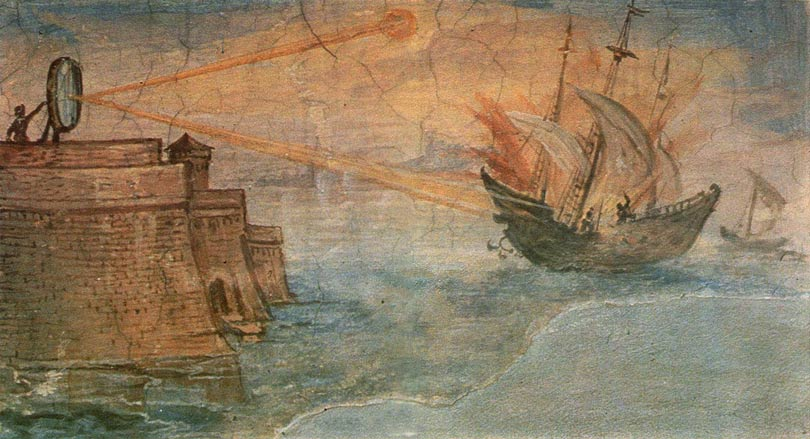

Heat beam to burn enemy ships
The credibility and veracity of this story has often been questioned, and a number of tests have been conducted to attempt to reconstruct this historical event, including two tests conducted by students from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the United States of America (MIT) from which this research team concluded That this could happen, i.e. not impossible, though a weapon of this kind would undoubtedly be extremely sensitive against even the smallest of clouds, and would require ships to be very close to being able to incinerate them.
Discovery Channel's science television program, Mythbusters, conducted two experiments to test the validity of these claims, concluding that the most these mirrors could do is simply distort the crews' vision.
Another idea related to the heat ray weapon was also developed during World War II by Nazi scientists, who created designs to make a “sun gun”, which included the use of a reflective mirror that is attached or connected to a space station, and they also calculated its strength and concluded that the sun weapon could This can burn an entire city or make the oceans boil, for more details on the topic see the article of the strangest weapons designed from here .
However, it did not stop here. Heat ray weapons continued to be developed in later times. In the early 2000s, the US Army created the Active Denial System (ADS), a non-lethal weapon created to disperse crowds. The demonstrator, controlling and controlling the situation for security purposes, and it works on the same principle as the microwave device by sending energy waves that lead to the stimulation of water and fat molecules in the human body or in his skin, which heat up instantly. Their skins were burning with fire.
The weapon was used in Afghanistan in 2010 by the US military, but it stopped being used in just one month, and it was criticized that it might be able to weaken its effectiveness by wearing a lot of clothes, as it was affected by weather conditions. ( Source 1 , Resource 2 , Resource 3 )
7. Rapid communication over wide distances:
In 1792, France had a network of signal poles consisting of 556 towers, which made it possible to communicate across the country.
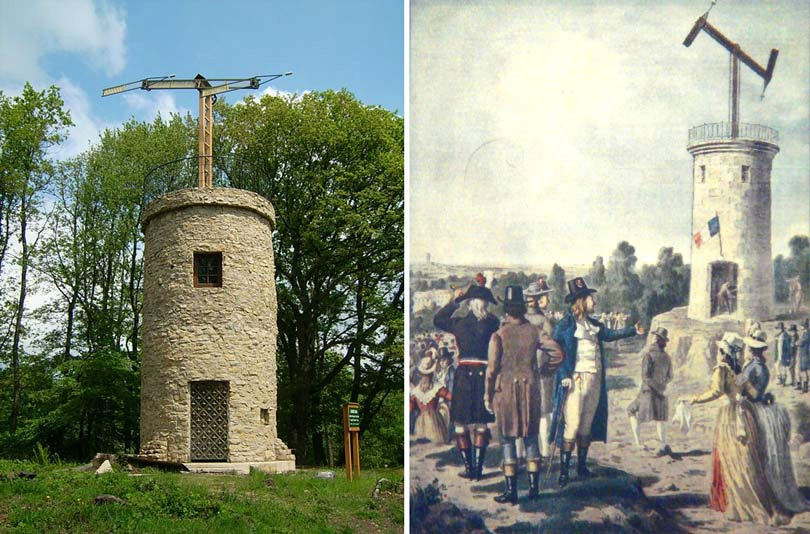

Signpost towers in 1792
Humans have communicated over long distances since ancient times, and even since the dawn of history, where ancient cultures used smoke and fire as communication signals, but the idea of communication by sending visual messages has been modified and developed with signaling telegraph devices, which dates back to the seventh century ten.
This idea included the use of a group of towers equipped with pivoting shutters, which through their arrangement allow the formation of different types of codes, and each tower passes the message to the next tower on the line, and France has developed a network of these towers over five thousand kilometers, which was developed for the purposes of Military warship, it gave the French army valuable information that was coming directly from the central government, which can now communicate directly with its various branches and pass orders.
Comparing it with the other method of communication over the long distances available at the time; The use of horses and their stations, signal tower lines were much faster, and this type of communication remained popular and common even after the invention of the electric telegraph in the year 1830, and it was not until 1846 that the French government began replacing optical signal towers with electric telegraph devices.
Although these telegraph devices have made communication over long distances significantly faster, and kept messages sent private, some have slandered them due to the fact that their lines are easy to cut. ( source 1 , source 2 )
8. Psychological warfare:
While leading the Mongol Empire that he founded in the thirteenth century, the Mughal leader “ Gengiz Khan ” invented some completely new ideas regarding psychological warfare methods, including the use of a type of arrow specially designed to make whistling sounds as a tactic intended to intimidate the enemy.
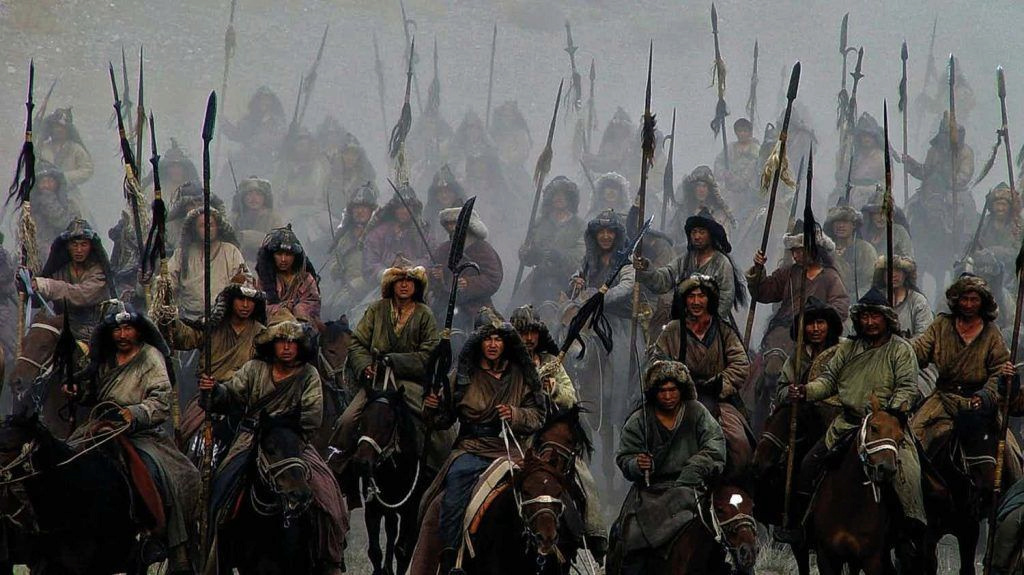

The first forms of psychological warfare were very simple, as the two armies were about to confront, the soldiers shouted and issued various loud sounds in order to frighten and intimidate the opponent, and Genghis Khan was the first to initiate the use of more advanced and more advanced forms of these psychological warfare.
For example, this commander resorted to a number of tricks and deceptions to make his armies appear larger and more numerous, including attaching objects to the horses' rears in the army, which leads to raising larger clouds of dust, in addition to ordering each of his soldiers to light three torches during the night.
The “Adham Khan” as they used to call him, used many tactical tricks designed specifically to frighten and intimidate the enemy, for example, his soldiers’ use of a type of arrow specially designed to make a terrifying whistle and a very frightening noise transmitted through the air, and this tactic was imitated from The German Army party during World War II when they equipped their aerial bombs with loud whistles in order to intimidate and intimidate enemies. ( source 1 , source 2 )
9. Cruise missiles:
The Kettering Bug is an unmanned aircraft and the direct predecessor of cruise missiles, which was developed by the US Army and made its first flights in 1918.
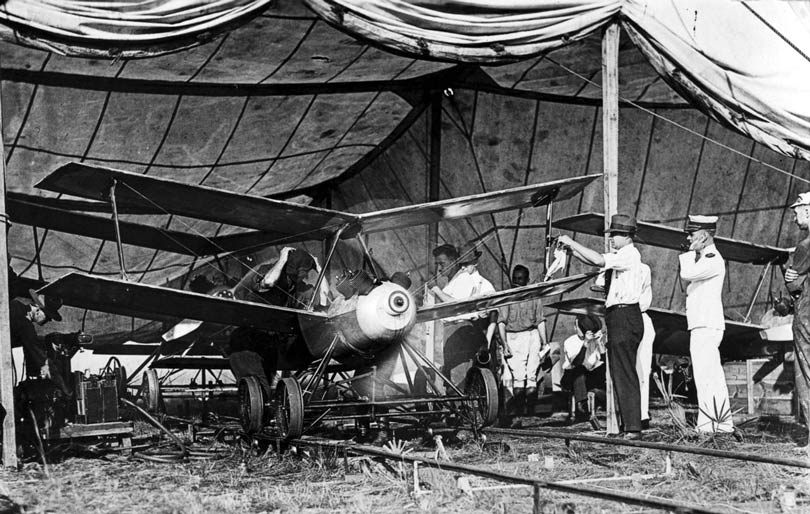

Plane Kettering Bug
The US Army Aviation Board asked Charles Kettering to build a flying bomb that could hit targets from forty-six kilometers away. Orville Wright worked on the project as a consultant, who with Kettering designed a drone with cardboard wings and a chassis The base is made of laminated laminate and paper mache, and uses a gyroscope to help guide it to its target locations.
In order to make the “bug” hit its targets when it reaches it, the technicians working on it calculated the number of engine revolutions required to hit this target. When an onboard counter reaches the required number of revolutions programmed to it; The engine is stopped automatically, and a set of screws are removed from the wings, which makes the wings separate from the bomb that falls directly on its target.
The insect was able to transport a payload of explosives weighing 100 kilograms, and the initial tests conducted on it showed promising success, as by the end of the war forty-five tests were conducted, but it was never used on the battlefield for fear of infecting friendly forces. ( source )
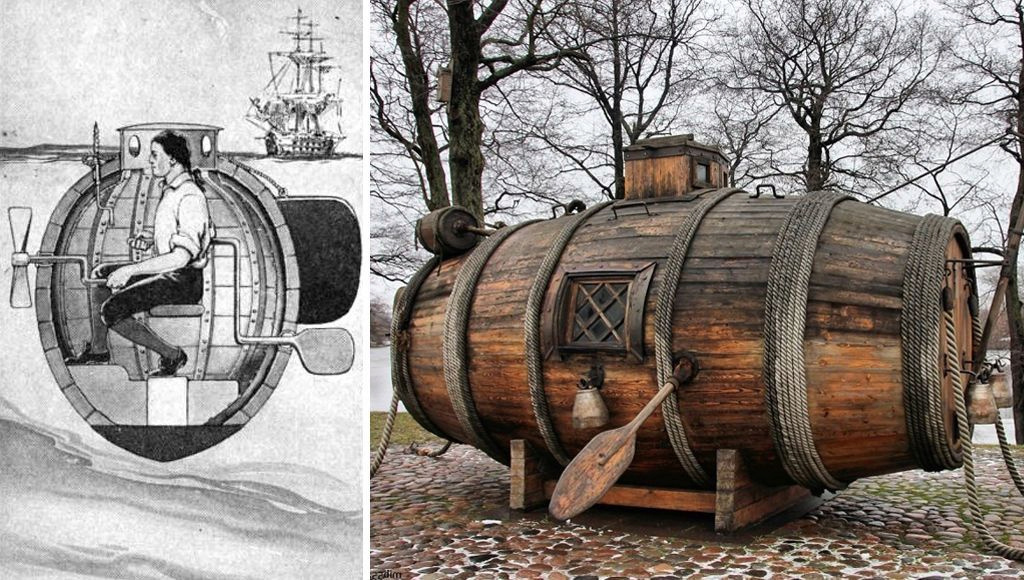
10. Military submarines:
The first successful submarine was built in England in 1620, and during a demonstration it remained submerged for three hours. It used raw minerals as a power source, and contained hoses attached to buoys to supply air to the crew.
About a hundred years later, in 1718, a Russian carpenter put forward his idea of the first warship to the Russian Tsar, “Peter the Great.”
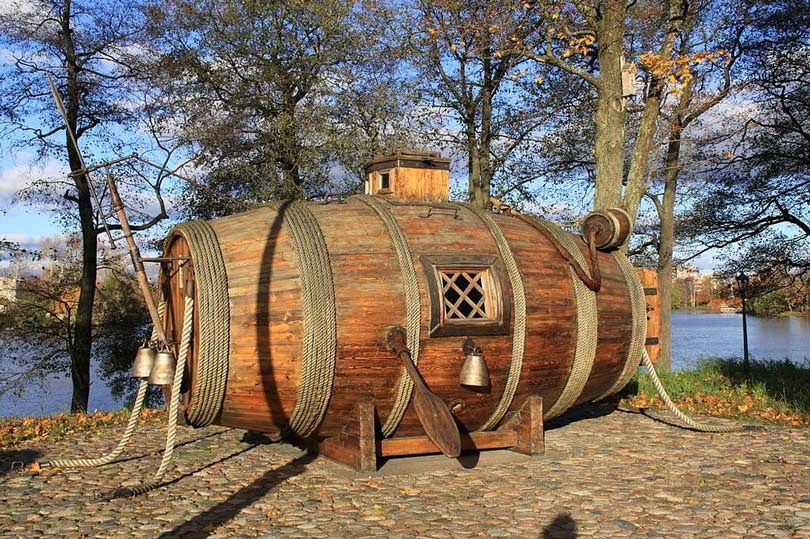

The first submarines in history
The design looked like a huge barrel, and this submarine was armed with “fire tubes” so it could approach enemy boats and eject the tubes above the surface of the water and then spray the boats with flammable materials. Destruction of the hollows and bottoms of enemy boats and boats.
However, the idea was abandoned after many failed tests and the death of "Peter the Great" the only proponent of the idea.
The second important milestone in the submarine industry came in 1776, when the American "David Bushnell" designed the "Turtle".
This turtle was egg-shaped, and used motors powered by hand propellers, but there is debate about whether the turtle was used in actual battles or not, although some American reports indicate that it was used in an attempt to connect a bomb to the bottom of a warship The mission was canceled when the submarine was spotted by the British ship.
Some historians believe that the reports about the turtle may be purely American promotional campaigns, as there was not a single British report about it. ( source 1 , source 2 )
Unbelievable-facts has compiled the information.
https://dkhlak.com/10-inventions-that-were-developed-earlier-than-you-think/?utm_source=Facebook&utm_medium=PostPlanner&fbclid=IwAR3ECpTYlhj3gMHomJbSoSib2a-G6cNHD2G6uYNl4EqdmhiiJ38A_cm_5e0

