Dart program: Can scientists deviate the path of asteroids targeting
? Earth

Less than 7 years from now, one of the greatest threats to life is expected to loom in the skies of Earth. Asteroid 99942 (99942 Apophis), 340 meters in diameter and 20 million tons of iron, was discovered in 2004 by the Kate Peak Observatory in Arizona. Its name is attributed to an evil snake mentioned in ancient Egyptian mythology, and it is a sign of an inevitable evil.
As the preliminary data showed, on April 13, 2029, the asteroid “Apophis” will pass near the Earth at a distance of 31,000 km, which is 12 times closer to us than the moon, and even closer than many orbiting satellites around the Earth. The asteroid will appear as clear as it will be available to the naked eye in broad daylight in a breathtaking scene as if the famous "Petronas" twin towers were flying in our sky.
And the matter does not end there. There is another problem that is more worrying. What astronomers call the "gravitational keyhole" - which are locations around the planets - that force the celestial bodies passing through them to return in the future due to the influence of the planet's gravity. If Apophis passes through one of these points, exactly 7 years later he will hit the Earth with an inevitable tragic accident, according to the calculations of celestial mechanics.

? Will the approach of the asteroid "Apophis" pose a threat to Earth
And what scientists initially found is that the rate of an asteroid collision with Earth in 2036 is 2.7%, which is a great risk whose evil is not guaranteed. So a state of alert was announced at the level of many of the institutions involved, and Apophis was put under the microscope. However, with later recalculations, it turned out that his threat was less than what was announced, despite his presence at a very close, unfamiliar distance.1
Thousands of asteroids.. lurking dangers
A meteorite of this size is capable of causing massive damage within hundreds of kilometers from the impact site, producing an energy equivalent to 1,000 megatons of TNT, which is 100,000 times more than the effect of the Hiroshima nuclear bomb.
And of the nature of the Earth and its relationship to meteorites throughout history, scientists believe that there are meteorites falling on the planet periodically at different time intervals, some of them every 100 years, including every 1000 years, and others over longer periods.
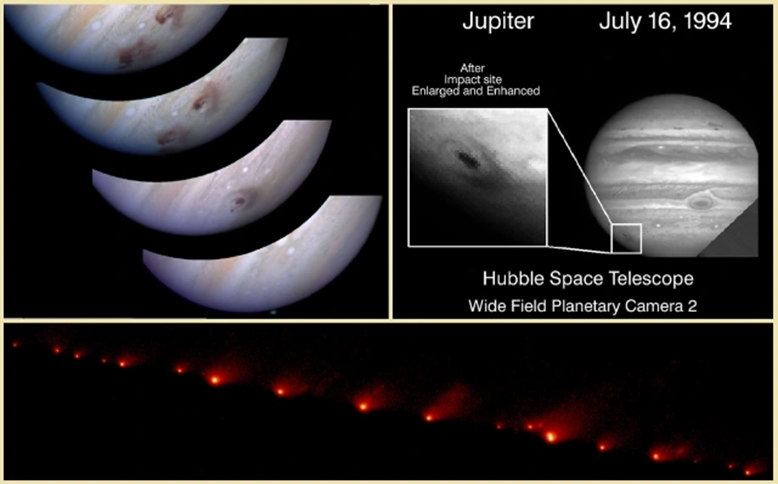
In 1994, 21 pieces of comet Shoemaker-Levy smashed into Jupiter and blew huge holes in its atmosphere.
In 1994, the Shoemaker Levy asteroid colliding with Jupiter created huge holes in the planet’s clouds, the size of the Earth or larger, and their appearance continued for several months before their disappearance, which sparked public opinion and prompted many to adopt a similar scenario on the planet, and then the disaster will come upon us. Without a doubt.
With government reinforcements, specialized centers have been established to study the asteroids that can be covered around the Earth, which number more than 750,000. Today, there are many observatories that contribute to enhancing these numbers, including the “Catalina Sky Survey”, which specializes in tracking small asteroids, and “Pan Stars.” (Pan-STARRS) to detect faint objects, and the Asteroid Last Alert System (ATLAS) scanner for spotting fast objects... Together, these observatories form an integrated system for observing the Earth's sky.
? Frequently asked question: Is our planet safe
In any case, knowing this alone is not enough, as scientists should revise and classify these celestial bodies based on how dangerous they are on Earth, in order to focus entirely on the source of the danger rather than distracting it, so the term "potentially hazardous asteroids" came up. To refer to it, and also the term for the objects in the near-earth orbit around the Earth (Near-Earth). The mechanism for classifying the asteroid’s danger is done by studying its size, orbit, and the extent to which it can meet the Earth in the future, and scientists believe that our planet is considered safe for the next 100 years at least, according to the figures available today.2

A comparison of the size of the asteroid Didymos, its moon Demorphos and the space probe DART with some features of the Earth
But what if it appeared on the far horizon from the meteor belt, for example, located between the planets Mars and Jupiter; Huge asteroid and threatened Earth in any way? Will the inhabitants of the planet stand idly by, or do they have a different opinion? This is what the Dart space program to protect the Earth answers.
"Dart" .. a probe plans to protect Earth from asteroids
The Binary Asteroid Trajectory Change Test (DART) probe is the first international space program aimed at defending Earth from the invasion of asteroids and meteorites that are believed to have led to the extinction of many living creatures on Earth in the past. The probe is sponsored by the NASA Planetary Missions Program Office.
Earlier, NASA, in partnership with the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, announced the launch of the first vehicle of the project by the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in September 2021, and the operation aims to test the effectiveness of the weapon adopted by the SpaceX program. "DART", which is the use of a collision probe that deviates the path of an asteroid or meteor.

Qatar is the only Arab country to participate in the Space Collision Imaging campaign, which is led by the European Space Agency
Without adding any ambiguity or complexity to the mechanism of the Dart program, it launches a space probe to a predetermined target in order to collide with it. Instead of detonating it, it will cause a small change in its movement or speed, just like billiard balls when one ball collides with others, causing them to be pushed. This is known as the "kinetic collision" effect, or the transfer of momentum from one body to another.
Despite the great disparity in the size of the probe and the size of the asteroid, a slight change will occur, but this will be enough to change the asteroid's path or delay it in the long term, as we are talking here about enormous planetary orbits that take months and perhaps years to complete their cycle.
Experimental impact.. Wait for the first operation of its kind
The spacecraft "Dart", launched by NASA recently, aims to test this technology for the first time, with a mass of 610 kilograms. /hour) the moment of impact.
The asteroid moon "Demorphos" with a diameter of 163 meters; Expected goal of this experiment. According to the calculations, the impact date is today, Monday, September 26, at 23:14 UTC, at dawn on Tuesday, September 27, at 02:14 Mecca time.
Accompanying the spacecraft will be a satellite called LICIACube, which is entirely made by the Italian Space Agency and contains only one scientific instrument that will image the target and guide the spacecraft at during the collision flight.
By studying the data later, it is expected that scientists will deduce the efficacy of this mechanism from the totality of mankind's attempts to defend their settlement on Earth. It is worth noting that the asteroid "Demorphos" with a diameter of 163 meters, which orbits around the asteroid "Didamos" with a diameter of 780 meters, does not pose a threat to us, and their orbit will not intersect with the Earth's orbit, according to the data, so the first experiment took place on it without risk.3
About 4 years after Dart's collision with Demorphos, the Hera spacecraft, in cooperation with the European Space Agency, will head to the site of the accident to study and assess the severity of the impact, measure the resulting crater, in addition to analyzing the celestial body's orbit and comparing it with its previous model before Impact, which will promote a broader concept of dealing with such cases in the future.

The space probe "HERA", which will be launched in 2024, will evaluate the results of the collision of the "DART" probe with the asteroid "Demorphos"
The Dart project is a paradox. Traditionally, engineers seek to protect their engineering products and spacecraft in various ways, but not here. The project is based on sending space ships whose main function is to collide with asteroids and meteorites floating in space in order to change their orbit.
In conclusion, the DART program is the first of its kind in confronting the danger from deep space. Despite our complete ignorance of the extent of its effectiveness, the attempt remains invaluable today in our race against time, and in light of the foggy space and our inability to comprehend it with every incoming and outgoing.
Sources:
[1] Mashhols, Don (2022). The asteroid Apophis will pass by us 7 years from now. Retrieved from: https://earthsky.org/space/asteroid-99942-apophis-encounters-2029-2036-2068/
[2] Website Editors (2012). NASA says that 4,700 potentially dangerous asteroids are located near Earth. Retrieved from: https://www.space.com/15734-dangerous-asteroid-census-nasa-telescope.html
[3] Smith, Wayne (2021). Six Questions with Dart Project Director Clayton Catchel. Retrieved from: https://www.nasa.gov/centers/marshall/news/releases/2021/dart-on-target-six-questions-with-mission-manager-clayton-kachele.html
[4] Michael, Patrick, Kupres, Michael, and Carneli, Lan (2018). Mission "Hera". Retrieved from: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2018cosp…42E2280M/abstract
https://doc.aljazeera.net/%d8%aa%d9%82%d8%a7%d8%b1%d9%8a%d8%b1/%d8%a8%d8%b1%d9%86%d8%a7%d9%85%d8%ac-%d8%af%d8%a7%d8%b1%d8%aa-%d9%87%d9%84-%d9%8a%d8%aa%d9%85%d9%83%d9%86-%d8%a7%d9%84%d8%b9%d9%84%d9%85%d8%a7%d8%a1-%d9%85%d9%86-%d8%ad%d8%b1%d9%81-%d9%85%d8%b3/?fbclid=IwAR06GAHAmg4piMd1pA4uUx4-laog6kHsyDvcabqpj_U5XsepEgDg12ZFYyc

