-supernova-
It is a huge astronomical event that occurs during the last stages of the life of every massive star, from the stars of the vast universe, where a stellar explosion occurs in the heart of the huge star, and as a result, the star throws its cover into the space around it in all directions, at the end of its life and this leads to the formation of a giant cloud Very bright, huge and spherical around the star, and so bright that astronomers can record it, and this cloud consists of plasma, which was forming the star's outer layer, as is the case with our sun..
The energy of the massive explosion, the supernova, spreads rapidly in the space surrounding the star's location, and turns into invisible objects after its bright brightness, after a short period of time.
? How does a supernova happen? Or a supernova
: The explosion of stars or supernovae occurs for two reasons
1_ Once the star's fuel runs out of hydrogen and helium
2_ If the star’s material and mass exceed the limit required for equilibrium, and in both cases the gravitational forces towards the center or the centrifugal force overcome, which leads the star to collapse in on itself internally, and its density increases to very high rates, towards the center. and turns into:
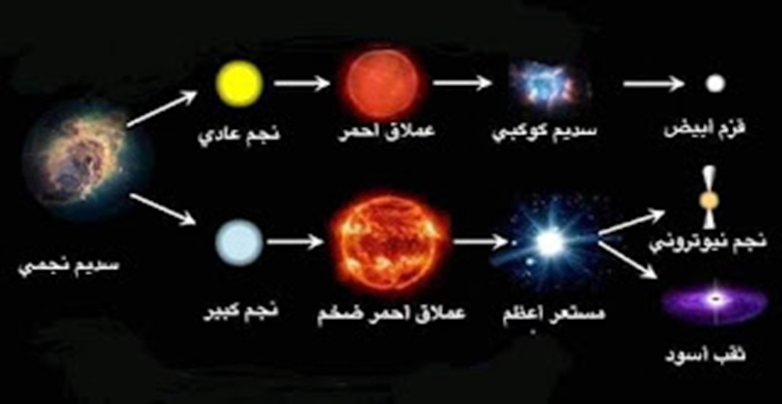
A white dwarf is a type of star.
Or turn into a super type, a neutron star
? What is a white dwarf
The white dwarf is the fate of the sun and our star, and every star has the same size and mass, and this happens after the nuclear fuel that fuels the fusion reaction has run out. When the star approaches the exhaustion of its fuel, a supernova occurs. In this type of star, most of its mass of matter is expelled into the outer layers. This leads to the formation of a planetary nebula around the location of the star and the high temperature of the core.
neutron stars
The central region of a supernova collapses when this happens under the influence of gravity; This gravitational collapse is so strong that the protons and electrons in the nuclei of atoms combine to form neutrons.
This is why they are called 'neutron stars' or neutron stars. Within the remnants of supernova explosions, neutron stars can appear as isolated stars or as binary star systems.
Some LIGO astronomers expect four neutron stars that they believe are orbited by planets. When a neutron star is a double and in a binary system, astronomers can easily measure its mass and know its size.
The transformations of stars in the case of a supernova depend on the mass of the star and the amount of its matter. If the mass of the supernova star exceeds 20 masses similar to the sun, it can turn into the most dangerous and mysterious cosmic body, a black hole, without exploding in a bright and intense way, as is done in Supernova image.
The end of life for stars, supernova
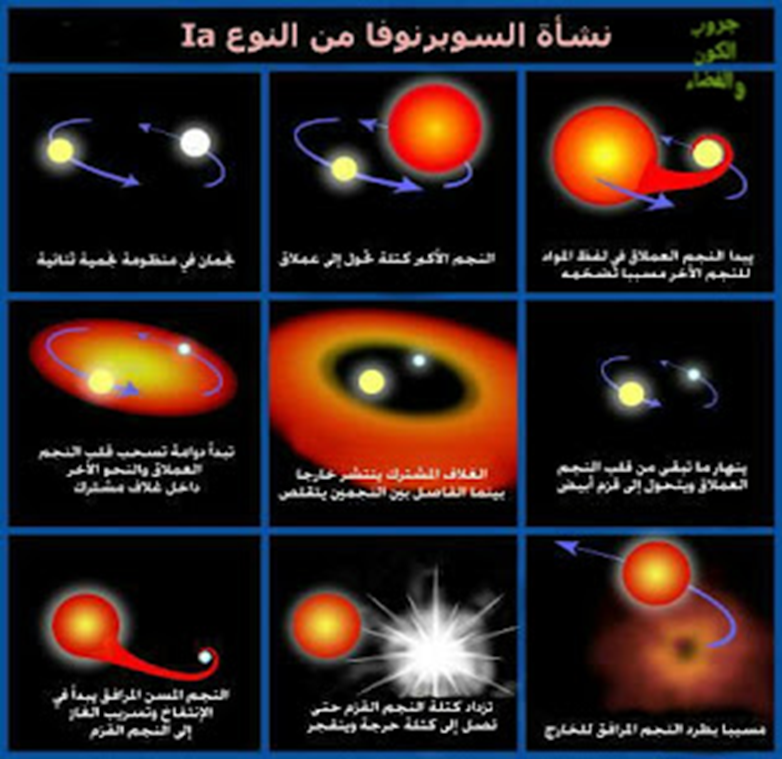
There are two possible paths to this end: Either a massive star greater than 8 solar masses ends up when the process of nuclear fusion ends in it due to the sudden depletion of nuclear fuel, gravitational forces prevail and the star collapses inward beneath. The effect of its gravitational force, a Type II supernova, and another possible path. A white dwarf picks up additional matter from a neighboring star until it reaches a critical mass, the Chandrasekhar boundary, and undergoes a thermonuclear explosion, a type I supernova. Or a neutron star, and the boundary between these two evolutions is 1.4 solar masses, and if the star’s mass is greater than 1.4 solar masses, then the star is going through a supernova phase
Supernova ratings
In an effort to understand the occurrence of supernovae, astronomers classify them according to their incoming absorption spectra, which form fingerprints that identify us with the chemical elements that make them up.
The first indication they use is whether or not the main gas is hydrogen in the supernova. If there is a line in the supernova spectrum from the group of hydrogen lines in the visible light spectrum of the spectrum, then astronomers classify it as a supernova II, otherwise they classify it as a type I supernova because of its presence. helium spectrum
types of supernova,
_ deceptive supernova,
_ double supernova,
- gamma ray burst ,
First, a deceptive supernova
It is a stellar explosion, but it appeared for the first observations. It appears as one of the types of supernovae, but it turns out that the main star has not yet been destroyed. It is a type of powerful supernova that lasts a long time, and it is called Type V supernova, an example of this nebula called Eta Base..
double supernova
A double supernova explosion occurs in stars ranging in size from about 130 to 250 masses similar to the sun, including newly discovered astronomical objects such as:
MA 2006 JY, ,,,, and MA 2213-1745 and likely represent the kind we're talking about in a double supernova.
- Gamma ray burst
Most gamma-ray bursts are seen as a narrow beam of intense radiation (jet) that is emitted during a supernova explosion, in a star with a high rotation rate (such as a pulsar), or when it is a large star. shrink (maybe 10-100). Also observed are solar masses forming a black hole, and short-lived gamma-ray bursts lasting only a few seconds, originating from another source, likely due to a binary star merger or the sudden contraction of a neutron star.
Source: websites