NASA Rover Finds "The Best Evidence Of Water" On Mars
NASA shared a snapshot from its Curiosity rover, revealing "compelling evidence" of water in an area of the planet that was previously thought to be a wasteland.
The rover, which has been exploring the Red Planet for more than a decade, has helped scientists understand a lot about Mars since it landed on its surface in 2012.
The recent discovery in a region of the planet known as the “sulfate-bearing unit” excited NASA scientists in particular, after they found “the clearest evidence yet” of the likely existence of a large lake in an area that was previously thought to have contained only small drops of water.
And the Curiosity rover recently discovered a wavy rock texture indicating the presence of lakes in an area of ancient Mars that scientists expected to be drier.
Billions of years ago, waves on the surface of a shallow lake moved sediment deep in the lake, and over time, this created an undulating texture left in the rocks, according to a NASA statement.
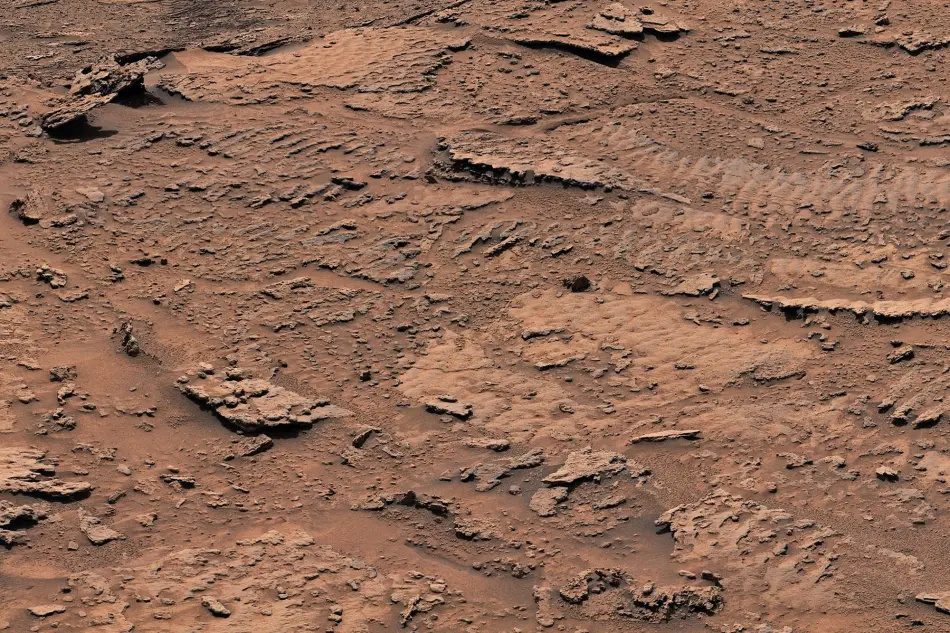

"This is the best evidence of water and waves we've seen on the entire mission," NASA's Aswin Vasavada said in a statement this week. We've climbed lake sediments thousands of feet and have never seen evidence like this. Now we found it in a place we thought would be dry.”
He assumes that if life, microbial or otherwise, ever existed on Mars, evidence of it would likely be discovered near where the water was once concentrated.
Scientists also expect to find clues about how the once watery planet turned into the frozen wasteland it is today.
However, efforts to dig up samples at the foothills of Mount Sharp, a three-mile-high mountain that once contained streams and lakes, have been complicated by the rover's encounter with hard-to-drill rock.
"The ancient Martian climate had a remarkable complexity, much like Earth's," Vasavada added.
The discovery of water on Mars was first confirmed by NASA's Phoenix Mars probe in 2008, and with subsequent missions scientists located a large subglacial lake about a mile below the southern ice cap in 2018.
Source : websites

