?At a speed of 800 km / sec, it is heading towards the Earth.. What is the solar wind and what is its danger
Scientists have detected the appearance of a second giant coronal "hole" on the surface of the sun, estimated at 20 times the size of the planet Earth, and said that it is about to send solar winds towards Earth that may reach a speed of about 800 kilometers per second, or 1.8 million miles per hour. And they expected that these winds would reach our planet on Friday or Saturday, and that they could create aurora borealis in some parts of the world.
Coronal holes are known to shoot solar winds into space, which can damage satellites and cause spectacular aurorae if they reach Earth.
Speaking to Business Insider, Matthew Owens, professor of astrophysics at the University of Reading, said: "The sun is preparing for its peak activity, which occurs approximately every 11 years. These holes are likely to appear near the sun's equator."
?What is meant by solar wind
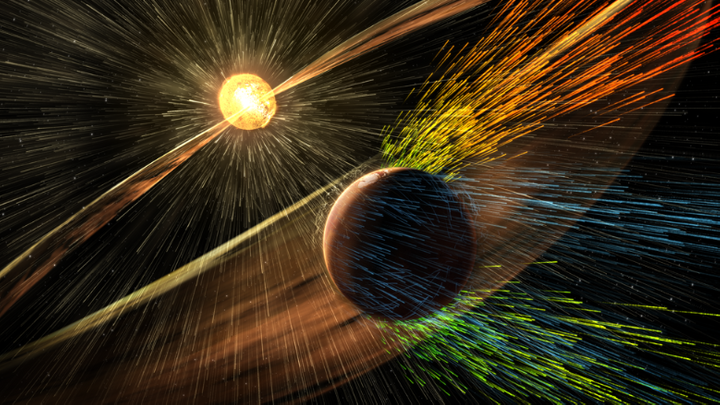
Not only does the sun send off heat and light, it also sends many other forms of energy and small particles on its way to our planet. One such form of energy is the solar wind, which is a stream of charged particles, mostly protons and electrons, continually emitted from the sun. It is a continuous flow of gas, plasma and magnetic fields that extends outward from the sun's corona into interplanetary space at a speed of about 400 km/s (or 1.5 million km/h).
This phenomenon was first observed in 1859 by astronomer Richard Carrington during a solar storm. But the sun does not send out the same amount of energy all the time, so there are constantly flowing solar winds and there are also solar storms.
During one type of solar storm called coronal mass ejections (CMEs), a huge bubble of electrified gas belches up and can travel through space at high speeds, potentially having a significant impact on our planet and its environment. While the strength and duration of the storm depends on the intensity and direction of the solar wind, as well as the direction of the Earth's magnetic field.
While the solar wind is not directly dangerous to humans living on Earth, it can have an impact on everything in the solar system, from planets to asteroids and comets. It interacts with planetary magnetic fields, causing auroras, and can even affect the trajectory of spacecraft, as well as our technological infrastructure.
Charged particles in the solar wind can interfere with and damage satellites, power grids, and communications systems. This phenomenon is known as a geomagnetic storm. In 1989 a particularly powerful solar storm caused power outages in Quebec and Canada, and disrupted communications and navigation systems around the world.
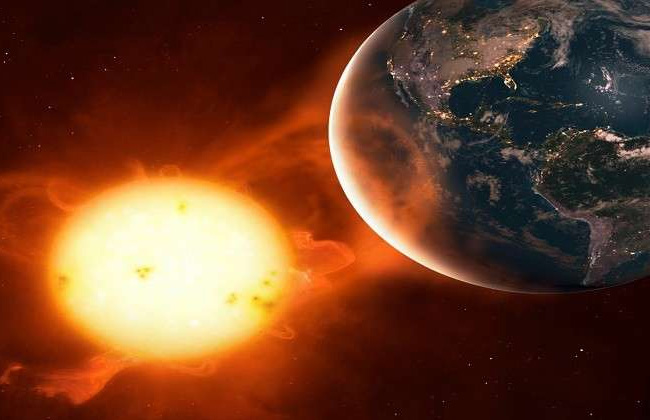

The solar wind can also pose a danger to astronauts and spacecraft. Charged particles in the solar wind can also cause radiation sickness and damage electronic equipment. NASA and other space agencies take precautions to protect astronauts and equipment during solar storms by monitoring the solar wind and adjusting spacecraft orbits accordingly.
In addition, the solar wind has the ability to affect the atmospheres of planets and moons. For example, the solar wind is thought to have stripped away much of Mars' atmosphere over time, leaving the planet with a thin, brittle atmosphere. Similarly, the solar wind has a significant impact on the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan.
People specially travel to the frozen poles, especially the northern ones, to see natural light shows called the "Aurora Borealis". The distinctive lights that appear near the North Pole are called the aurora borealis or the northern lights, while those near the south pole are called the aurora borealis or the southern lights.
Although it is better to see the aurora borealis at night, it is caused by the sun, and specifically by the solar wind that coronal holes release from the surface of the sun. While the magnetic field around the Earth protects us from most of the energy and the particles it sends, we don't even notice it.
When a solar storm comes towards our planet, some energy and small particles can travel through the magnetic field lines at the north and south poles into the Earth's atmosphere. There, molecules interact with gases in our atmosphere, resulting in a beautiful light show in the sky. While oxygen gives off green and red lights, nitrogen glows blue and purple.
Source: websites

