Here are 25 facts you did not know about Djibouti
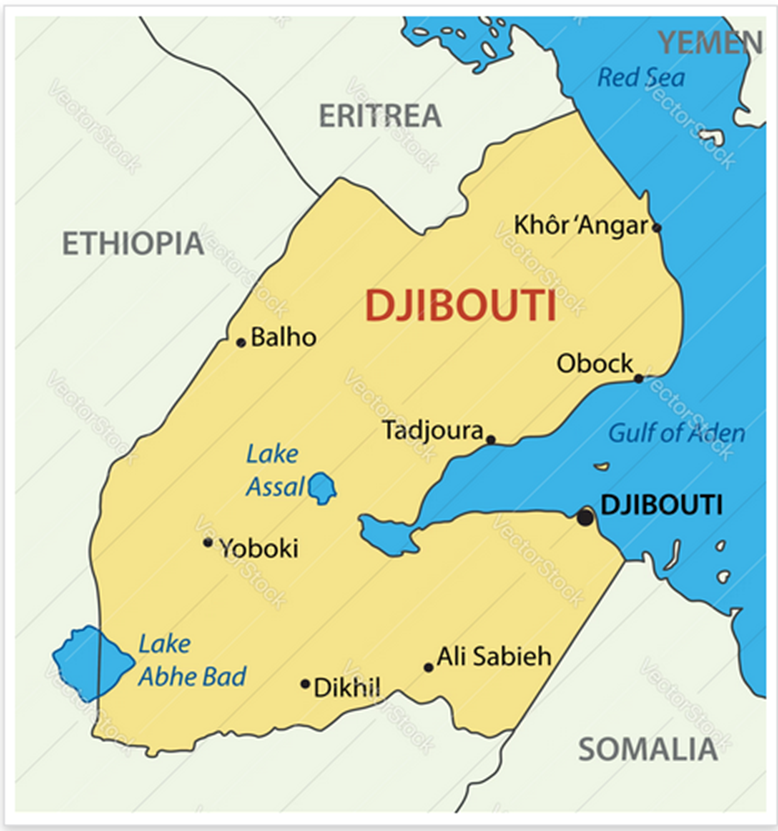
Djibouti is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Ethiopia to the west and south, and Somalia to the southeast.
Its capital is Djibouti City, which is also the largest city in the country.
The official languages of Djibouti are French and Arabic.
Djibouti was under French colonization until its independence on June 27, 1977.
Djibouti is one of the smallest countries in Africa in terms of area and population. Its area is about 23,200 square kilometers. The population of Djibouti is about 1.1 million people.
The national currency is the Djiboutian franc.
Djibouti is considered an important strategic location because it is located on the Bab el-Mandeb Strait, which connects the Red Sea to the Gulf of Aden. The port of Djibouti is one of the most important ports in the region, and is used as an international naval base.
The salt lake in Djibouti, Lake Assal, is the saltiest lake in the world after the Dead Sea.
Djibouti's climate is hot and dry most of the year.
Most of the population in Djibouti follows Islam.
Djibouti has a diverse terrain that includes deserts, mountains, and coastal plains.
Djibouti relies heavily on imports to meet its food needs.
Djibouti has a US military base known as Camp Lemonnier.
The economy in Djibouti depends mainly on services, especially maritime transport and communications.
Djibouti is a major stopping point for international airlines due to its strategic location.
The Djiboutian government is investing in infrastructure development, including railway and energy projects.
The literacy rate in Djibouti is relatively low compared to other countries in the region.
Djibouti is a member of the African Union, the League of Arab States, and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation.
Djibouti is distinguished by its unique geological location at the intersection of three tectonic plates: African, Arabian, and Somali.
Livestock plays an important role in Djibouti's rural economy.
Groundwater in Djibouti is an important resource for rural residents. Despite its small size, Djibouti has great biodiversity. Djibouti has some distinctive tourist sites such as the Tadjoura region and the Gouda Mountains.
Traditional dances and music play a large role in Djibouti's culture.
Djibouti was formerly known as "French Somalia".
The people of Djibouti consist of two main ethnic groups: Somalis and Afar.
Djibouti enjoys strong diplomatic relations with many major countries, especially the United States and France.
Source: websites

