In illustrations.. this is what the five pictures of James Webb tell us about the universe

On Tuesday, July 12, the US space agency "NASA" published the first set of high-resolution color images obtained from the giant James Webb Space Telescope, which cost about 10 billion US dollars.
Taken together, the images represented an amazing cosmic show that captured the breath of millions of people around the world
The images of the James Webb telescope represented a stunning cosmic show in every sense of the word, capturing the breath of millions of people around the world as they watched scenes from the deep universe, never seen by humans, that contain signs of cosmic accidents that occurred billions of light years ago, from the collision of galaxies and the dying of stars and the birth of other , the clouds and the cosmic spectra of the outer planets, and the signs of abyssal universes in space, which after these images will not remain a mere speck of blackness.

It seems that the telescope has achieved better results even than the scientists who worked on developing and building it over the past three decades in the United States, in cooperation with the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency, dreamed, thanks to the reliance on near-infrared technologies to detect dark depths. From space, and knowing the state of the first galaxies at points close to what scientists believe to be the beginning of the universe, or the moment of the Big Bang, about 14 billion years ago. John Mather, the famous Nobel Prize-winning scientist and one of the most prominent workers on the James Webb project since 1995, said after the first photos were published that he had seen things in them that he did not even know existed and that any monitor of any size could detect.
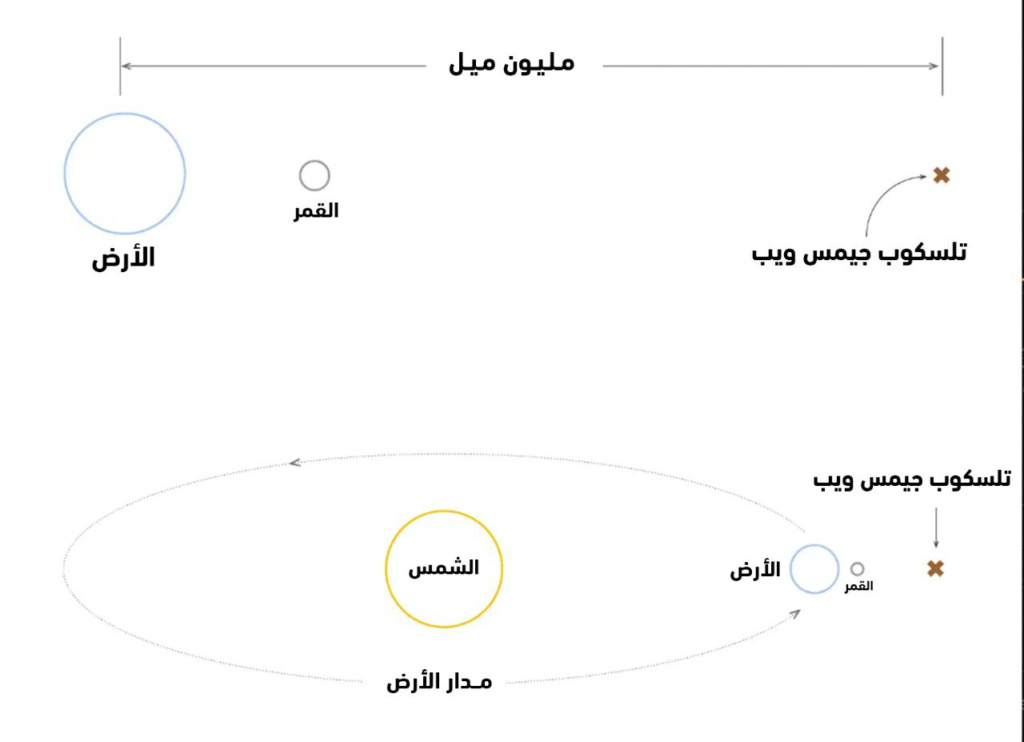
Where is the James Webb Telescope located?
Every detail about the James Webb Telescope is impressive. The telescope is the size of a tennis court. It cost more than $10 billion to build, develop and send it into space, and took at least three decades to set up. Scientists sent this massive space telescope to a point in space four times farther from the point where the moon is, that is, a million miles from Earth (1.5 million km), and it was placed in orbit around the sun in order to take unique images of space that allow us to see and analyze it in an unparalleled way. It was previously available to humans.
What do the five James Webb telescope images say?
1. The first deep space field
The first image, which was revealed at a special event at the White House in the presence of US President Joe Biden , sums up much of what can be said theoretically about the superiority of the James Webb Space Telescope, the results of which have been described as at least twice as good as previously expected. This image is known as the "first deep field", and it is a huge space image in which the monitor gazes at a patch of space the size of the universe, close to the size of a grain of sand when you look at it an arm's length from the eyes of the beholder. And this huge picture is just a glimpse of what this revolutionary monitor can reveal in the coming months, according to what the famous American astronomer Heidi Hamill confirmed .
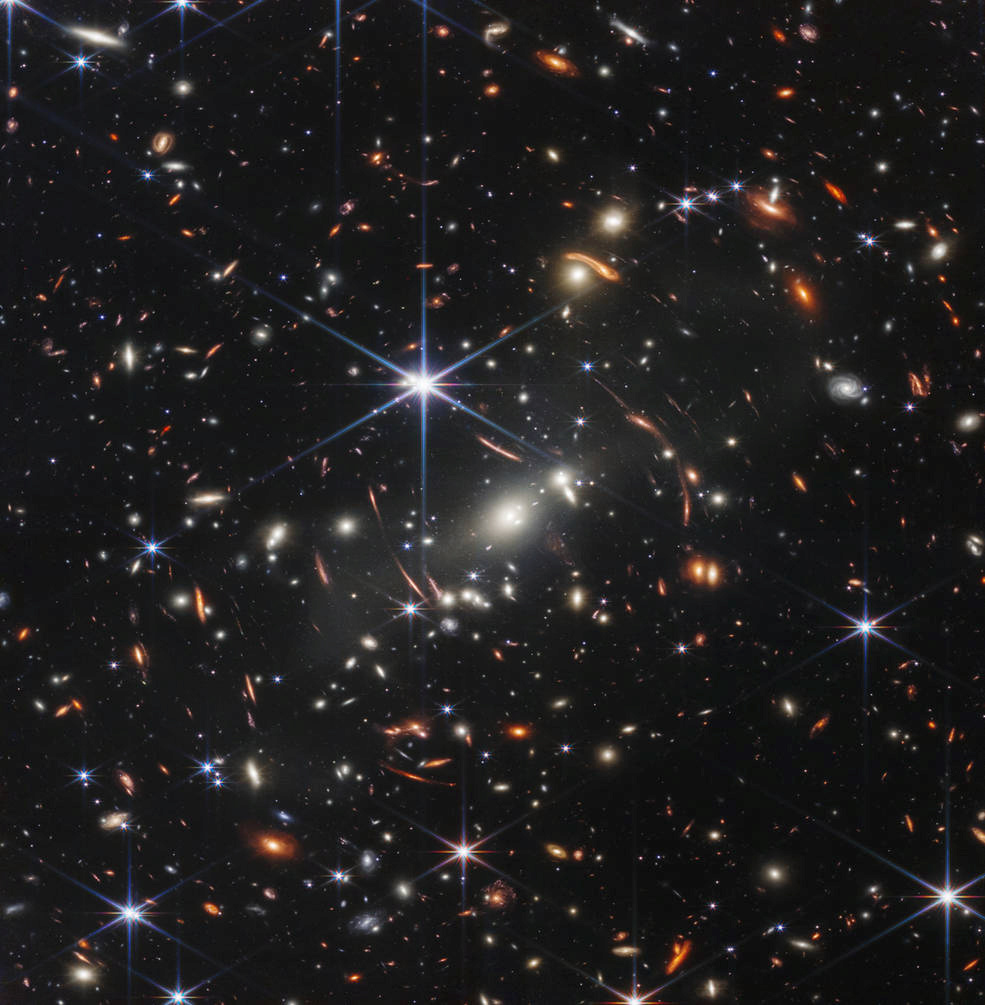

Most of the colored dots and spots in this image are galaxies, not stars , and each galaxy may contain billions of stars and planets. And this square that appears in the picture in front of you, is like the size of a grain of sand an arm's length from your eye. Always remember this analogy when you look at images like these from the James Webb Monitor. This image presents the oldest and highest-resolution image of the universe ever made.
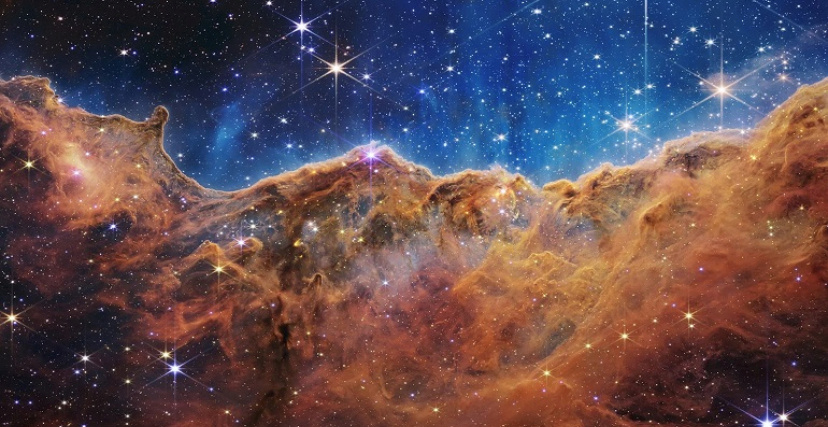
2- The Carina Nebula
The Nebula is a giant cloud of cosmic gas and dust in which stars are born, and this nebula that appears in the image is called the Carina Nebula .

The Carina Nebula is one of the largest star formation regions in the Milky Way, and is about 7,600 light-years away from Earth, meaning that traveling at the speed of light from Earth to this region will take 7,600 years, and this means that what appears in front of us in the picture is not the Carina Nebula as It appears the moment it was captured, as it was 7600 years ago, the moment the light recorded by the James Webb Telescope emitted from the source.
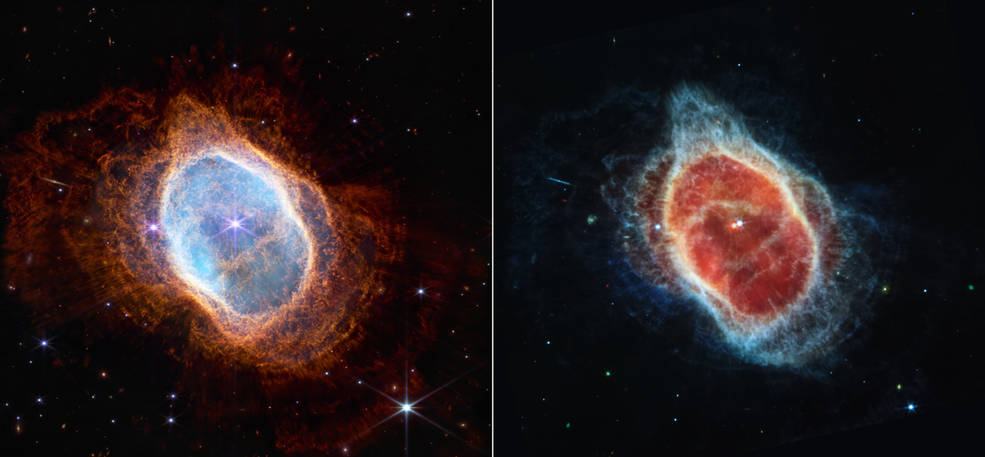
3. The Southern Ring Nebula
This planetary nebula is half a light-year long, 2,000 light-years away from Earth, and is called the Southern Ring Nebula. This high-resolution image shows us what the star looks like when it is dying.

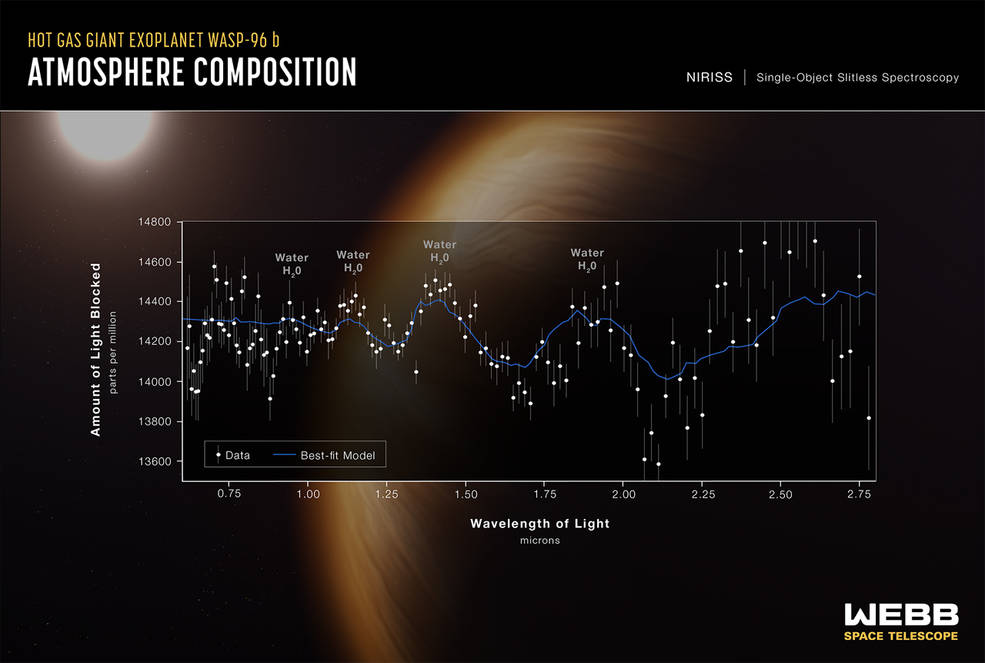
4. WASP-96 b . spectrum
This is a giant gaseous exoplanet, orbiting a star 1,150 light-years from Earth, so close to the star that it orbits in just three and a half days. The telescope was only able to photograph the spectra of this planet, which may indicate the presence of water in the planet's atmosphere, and that it is most likely surrounded by clouds and fog. It is possible to benefit from the technology that was used in imaging this spectrum in order to study the atmospheres of smaller rocky planets orbiting stars in closer regions in space, where water can be found on their surface, as is the case on Earth.
5. Stefan's Quintet
In this image, five galaxies are shown, as they are numbered below, and they are very close to each other, two of them are approaching the stage of overlapping or colliding and forming new stars. Younger stars appear blue, and older stars appear red.

In addition to these five amazing images above, which are truly a great achievement for humanity to allow scientists to explore, study and know about the vast universe, the James Webb Telescope also makes it possible to collect important data on the chemical composition of stars and planets outside our solar system, information that will help Shaping new approaches to the question of life elsewhere outside the Milky Way.
https://www.ultrasawt.com/%D8%A8%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B1%D8%B3%D9%88%D9%85-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%D9%88%D8%B6%D9%8A%D8%AD%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D9%87%D8%B0%D8%A7-%D9%85%D8%A7-%D8%AA%D9%82%D9%88%D9%84%D9%87-%D9%84%D9%86%D8%A7-%D8%B5%D9%88%D8%B1-%D8%AC%D9%8A%D9%85%D8%B3-%D9%88%D9%8A%D8%A8-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AE%D9%85%D8%B3%D8%A9-%D8%B9%D9%86-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%83%D9%88%D9%86/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AA%D8%B1%D8%A7-%D8%B5%D9%88%D8%AA/%D8%AA%D9%83%D9%86%D9%88%D9%84%D9%88%D8%AC%D9%8A%D8%A7

