Scientists discover a brain network capable of responding to different languages of the world
Discovery of a unique brain network that responds to speakers of all languages in almost the same way (websites)
An international research team led by scientists from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology was able to discover a unique brain network that responds to speakers of all languages in almost the same way, bringing back to the scene the question of the nature of linguistic diversity among humans, and its biological and cultural aspects.
brain regions
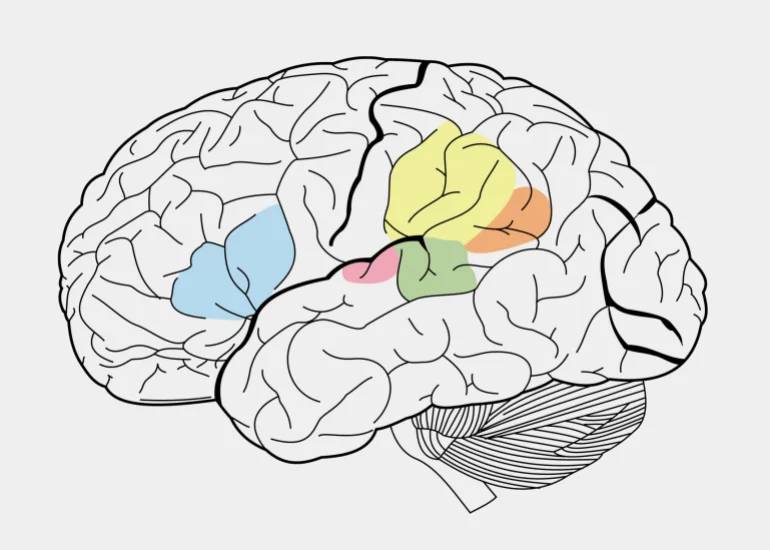
For more than a century and a half, scholars have known that there are two brain regions responsible for the language process ; The first is Broca's area, which is located in the dominant side of the frontal lobe of the human brain and is responsible for the construction and pronunciation of words.
As for the second, it is the Wernicke area, located in the back of the temporal lobe of the brain, and is often associated with language comprehension, that is, the sensory interaction with the language incoming to the brain, whether written or audible. Therefore, Wernicke’s area deals with “incoming” speech, while Broca’s area It deals with the "outgoing" speech.
But the various neural networks in these regions need more scrutiny to understand their essential role in dealing with language, and here comes the role of the new study published by the team in the journal Nature Neuroscience on July 18, 2022.
On the left in blue the area of Broca, on the right in green the area of Frenic responsible for language (websites)
language exam
According to the study, the researchers asked 45 people who spoke 45 different languages, but in total they join under 12 language families; Perform language tasks while their brains are scanned using functional magnetic resonance imaging.
The study hypothesized that only listening to or reading sentences in the mother tongue would activate the target language network. To distinguish this network from other brain regions responsible for language, the researchers also asked participants to perform additional tasks such as listening to unfamiliar language or solving math problems.
The researchers used 24 short texts and 3 long texts from "Alice in Wonderland", because it is one of the most translated literary works around the world, and each was recorded by a native speaker.
According to the new study, the team found that the participants' neural-linguistic networks were located in roughly the same brain regions, and had the same selective features and frequencies when they were activated.
It also appeared that the amount of difference between speakers of different languages is the same among speakers of the same language, despite the clear differences in languages in the order of words and the nature of grammar and time between words or sentences, which confirms the universality of that region of the brain.
According to a press release issued by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, this team is currently working on a more scrutiny of these results, whether by adding more languages to confirm the universality of the language network, or studying all parts of that particular network, in the hope of finding slight differences related to each language in a way. Special.
Source : websites
https://www.aljazeera.net/news/science/2022/7/31/%D8%A7%D9%83%D8%AA%D8%B4%D8%A7%D9%81-%D9%85%D8%B1%D9%83%D8%B2-%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D9%8A-%D9%84%D9%84%D8%BA%D8%A9-%D9%81%D9%8A-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AF%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%BA