Does the term central Morocco and its western borders mean the ?current state of Algeria
When you look at the Arab and Islamic history books that pertain to North Africa or the so-called Amazigh countries, we find that Arab historians and others used the term Africa, which means Tunisia now, and the term Middle Maghreb, which currently represents the state of Algeria and the term Al-Aqsa Maghreb, which later became a kingdom Morocco Al Aqsa
We also sometimes find in those old references the use of the term “Maghrib” and it refers to all the countries from west of the Nile River to the Atlantic Ocean, as mentioned by the Nasserite historian in his book “The Investigation.”
Where the term Maghreb was applied to all the Northwest African region from present-day Libya to Tunisia to Algeria to the Far Maghreb, but in another place it divided them into African countries (Tunisia and part of Libya), the countries of the Middle Maghreb and the countries of the Far Maghreb. Moulouya River
To warn, many semi-historians, especially the followers of the Alawi Al-Qumji Al-Arabi Makhzen, spread the fallacy that the name of the current Kingdom of Morocco has existed for more than 12 centuries, and this is a lie. Regions and emirates under the name of the honorable Kingdom of Morocco, including the Kingdom of Marrakesh, the Kingdom of Fez and the Kingdom of Sijilmasa
And you can see the first constitution of the current Kingdom of Morocco, which decided to name all the inhabitants of the Mamluks of Marrakesh, Fez and others after the name Moroccans.
This is in a book published by the researcher Professor Mohamed Nabil Mouline, in the past few days, entitled “The Idea of the Constitution in Morocco,” which is documents and texts documenting the constitutional history of the Kingdom of Morocco between 1901 and 2011.
A link to view the first constitution of the Kingdom of Morocco
https://www.noor-book.com/book/internal_download/27e9cb34ExSkh4
You will find in this constitution that the first time it was decided to name the Kingdom of Morocco as a state that brought together several different emirates was in the year 1809 AD.
It was also decided to call the residents of Marrakesh a Moroccan name, but this constitution was abolished under the protection treaty on Morocco in the same year.
The first constitution for the current Maghreb was in 1908 , when it was issued by the newspaper “Lisan al-Maghrib” published in Tangiers in the same year. You can see in the picture that the newspaper until 1908 AD called the Far Maghreb region after the Sultanate of Marrakesh and not the Kingdom of Morocco.
On this basis, the name and term Maghreb in the ancient references should not be confused with the term of the modern Kingdom of Morocco
And in this regard, we offer you the evidence from the admirer in summarizing the news of Morocco . A book on history written by Abd al-Wahed al-Marrakchi around 1225 AD
The historian Marrakchi explained that the term Maghreb means a geographical region in his time and not a state or kingdom.
For your information, at the end of the third century AH, the Maghreb countries were distinguished by the presence of two sides:
- The African side, meaning Tunisia at present, and its base is Kairouan.
The western side extending from West Africa to the surrounding sea.
This was indicated by Abu Al-Abbas Al-Yaqoubi, who called the second western side the name of Morocco without adding or distinguishing politically, ethnically or geographically. The same concept continues among the geographers of the fourth century AH (10 AD), such as Al-Istakhri, Ibn Hawqal, and Al-Maqdisi, i.e. the general nomenclature, which is the western countries, applied to everything that follows Ifriqiya and Tunisia in the west.
Beginning in the fifth century AH, the distinction appears between two parts from the western side of the present region of Tunisia, namely, the Middle Maghreb and the Far Maghreb, and they were widely used throughout the Middle Ages. The first of this distinction is found by the geographer Al-Bakri in the fifth century AH, when he described the city of Tlemcen by saying: "This city is located at the base of the Middle Maghreb ... and it is the home of the kingdom of Zenata and the middle of the Berber tribes."
In the book of the traveler and historian Abu Obeid al-Bakri, who died in 1094 AD, that is, before the emergence of the Almohad state, he mentions to us in his book Al- Maghrib in mentioning African countries and Morocco is part of his book Routes and Kingdoms page 76 paragraphs (mentioning the city of Tlemcen and what referred to it to Morocco)
The city of Tlemcen is the capital of Central Morocco, and therefore Central Morocco from the west, its borders were the city of Tlemcen, which is the same as the borders of the current state of Algeria
What are the borders of the middle Morocco and does it represent the state of Algeria now?
It came in the book Kitab Al-Istisar fi Aja`ab Al-Amsar by an unknown author from the 12th century CE
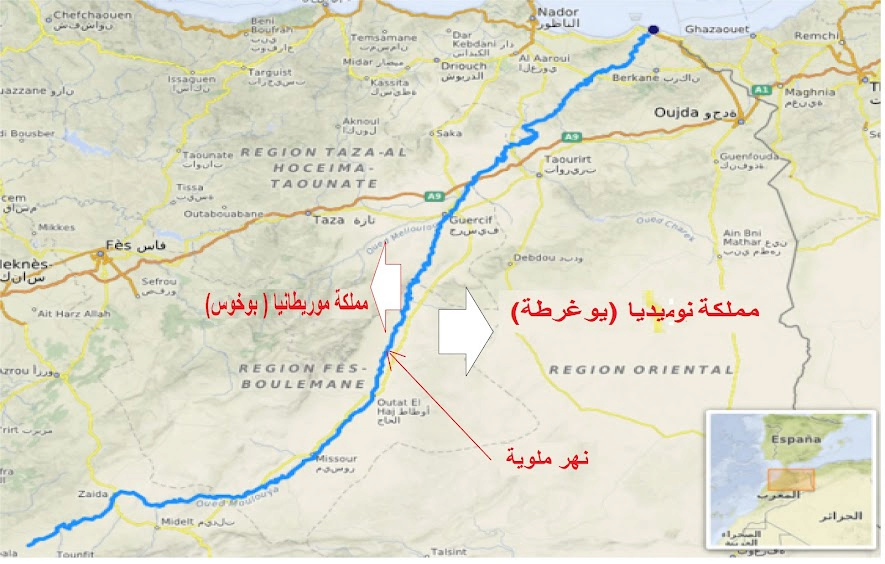
The central Morocco has its base in the city of Tlemcen, and from the northern coast, its borders reach the city of Melilla. It was also mentioned that the city of Oujda is among the cities of Central Morocco and the city of Agersif on the Moulouya River
https://www.noor-book.com/%D9%83%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%A8-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A7%D8%B3%D8%AA% D8%A8%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D9%81%D9%8A-%D8%B9%D8%AC%D8%A7%D8%A6%D8%A8-%D8%A7 %D9%84%D8%A7%D9%85%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D9%84%D9%85%D8%A4%D9%84%D9%81-%D9%85 %D8%AC%D9%87%D9%88%D9%84-%D9%86%D8%B3%D8%AE%D9%87-%D8%AB%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%8A %D9%87-pdf
As for the traveler historian Al-Idrisi , who died in the year 1164 AD , he mentions to us in his book Nuzha Al-Mushtaq
The Middle Maghreb has the following cities:
Constantine, Jijel, Setif, Bejaia, Djazair Ben Mazana, Tlemcen, Oran, Oujda, Melilla, Tiaret, Muqrin, Naqas, Batna, Msila, Yagai Khenchela, and the historian said that the Berbers (Amazighs) prevailed over these lands.
The words of the historian Al-Idrisi from the 11th century AD show that the term “Middle West” represented what is now known as the state of Algeria
On the other hand, Ibn Khaldun mentions in the 14th century AD in his book Al-Abr, Volume 6, the following:
As for the Middle Maghreb, it is mostly the lands of Zenata. It was for Maghrawa and Bani Yafran, and they had debts, Mughila, Kumiya, Mughra and Matmata, and then came after them Lubna and they died and Bani Yaloumi then became Lubna Abd al-Wad and Tujen. Whoever built what religion and his base for this covenant is Tlemcen, which is the house of his king, and its neighbors from the east side are the countries of Sanhaja, from Algeria, Miha, and Almeria and what follows it to Bejaia
Ibn Khaldun also says in the Book of Lessons, Part VI, that the term Morocco in the old references means the region from the Nile River to the Atlantic Ocean, and that this means a geographical area in relation to the Arab Mashreq, and that the Maghreb region is the maximum from the east is the Moulouya River, which lies west of the Tlemcen region Currently in Algeria
Also in the sixth part of the Book of Lessons by Ibn Khaldun, he says that Oujda and Bani Yazansen, which is now part of the Kingdom of Morocco, were part of the Middle Maghreb.
Quoted from Ibn Khaldun
Then Youssef bin Tashfin rose in the year four hundred and seventy-three after that to the countryside and conquered Gursif, Melilla and the rest of the country of the countryside and destroyed the city of Nkur, so it did not live after him. Al-Abbas bin Bakhti, the Emir of Tlemcen, was killed, and Muhammad bin Tigmar, who was satisfied with it, was sent to the soldiers of the Almoravids, and it became an outpost for his kingdom. He encamped with his soldiers and overtook the city of Takarrat in the place of his camp, which is the name of the locality in the language of the Berbers. Then he opened the city of Tennis, Oran, and Mount Wanchris to Algeria, and turned back to Morocco, and occupied Marrakesh in the year four hundred and seventy-five, and Muhammad bin Tigmar was still governor of Tlemcen until he died, and his brother Tashfin succeeded him.
is over
https://al-maktaba.org/book/12320/3661#p1
As for Leon the African, in his book Description of Africa between the 15th and 16th centuries AD
, he mentioned that the city of Tlemcen, the capital of the Zayan Kingdom of Tlemcen belonging to the Central Maghreb, had its borders up to the Moulouya River.
And when the Turks invaded the Central Maghreb in the 16th century AD
It was stated in the memoirs of Khair al-Din Barbarossa, page 86, that the city of Tlemcen is part of the country of Algeria
The historian Marmol Karbalach from the 16th century AD also mentioned that the Kingdom of Tlemcen is the third of the Berber kingdoms, and it was called Mauretania Caesar’s foot
, and that its western borders are the Kingdom of Fez, and the two kingdoms are separated by the Ziz River and the Moulouya River.
According to Marmol Karbalach in the 16th century AD, i.e. with the beginning of the Turkish occupation of Algeria and Central Morocco, the political and geographical borders were as in the following picture
. This border is located between the Central and Far Maghreb and separated by Wadi Moulouya within the northern facade, and it was brought south by the foresight to the city of Tizel, which is A city in the beginning of the desert and on the road to Sijilmasa, and this is for the Central Maghreb, as for the Far Maghreb, it goes to the country of Moulouya and its Ahwaz, i.e. the first country of Sijilmasa to the desert, and after that we do not find borders or separators in the desert between the two Maghreb. This corresponds to the words of Marmol Karbalach
Historically, the Moulouya River, located on the northern border of the present-day state of Morocco, was the boundary between the Berbers of Morocco
Al-Aqsa and the Berbers of Central Morocco, which is now known as the State of Algeria
It was mentioned in the book of the Roman historian Sallust of the first century BC, which was entitled "The Jugurtha War". where he says
“When the Jugurtha war broke out, the latter was the king of the Berber peoples of Numidia and the Gitol in the territory of present-day Algeria up to the Moloka River (Mulwiya River in the Kingdom of Morocco). as a friend.”
Almost all the Getulians and Numidians down to the Mulucha River were subjects of Jugurtha. All the Moors had for king Bocchus, who only knew the Roman people by name, and whom we ourselves did not know as enemy or as friend. Of Africa and its inhabitants, I said all that was necessary about me.
Read the book, Jugurtha war book by the Roman historian Sallust. (French)
Complete Works of Sallust
https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k58100377/f79.item.texteImage
second link
https://web.archive.org/web/20060913000000/http://fr.wikisource.org:80/wiki/Jugurtha_War
For caution , the Greek and Roman authors mentioned the Libyan population farthest to the west, which they called the Moors, and did not call them the Numidians, but this distinction did not achieve its final consolidation until the Romans learned of the existence of a local Berber kingdom in the Far Maghreb. In the second century BC, Artemidor was still bringing the Libyans living near the Pillars of Hercules in southern Spain into the Numidians. However, it is possible that the distinction between the Numidians and the Moors is older, if it is true that the name of the Moors, and the Numides as it is generally accepted, was no more than a geographical name and not an ethnic nationalism or a separate Berber tribe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Artemidorus
https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Art%C3%A9midore_(g%C3%A9ographe)
In the third century BC, the Kingdom of Numidia was divided into two parts:
1. The Kingdom of Western Numidia (Kingdom of Mazisel).
2. Eastern Numidia Kingdom (Kingdom of Almasil).
1 - Kingdom of Western Numidia (Almazysil): attributed to the tribes
Masaesyles _ (who appeared as a force since the late third century BC and early The second century, during the Second Punic War, which was headed by him at the time King Syafix, whom Titus Ephesus called "the most powerful king in all of Africa."
The borders of his kingdom extended according to Strabo, which is dated from the first century BC, from the valley of Malwiya ( Molochath ).From here we note that this kingdom belonging to the central Maghreb region, which is Algeria today, was covering a large area, extending from the Moulouya River, east of the present Kingdom of Morocco to the Algerian east
After entering it, there are [on the coast of Libya] a number of towns and rivers up to the river Molochath, which serves as the boundary between the territory of the Maurusii and that of the Masaesylii. The name of Metagonium designates both a large promontory near the mouth of this river, an arid and poor district, and, if need be, the whole chain of mountains which starts from the Coasts and extends as far as here. The distance from the Cape of the Coasts to the border of the Masaesylii represents a length of 5000 stadia.
Link to reading Strabon's book see paragraph 2
STRABON
GEOGRAPHIE.
LIVRE DIX-SEPT CHAPITRE III
http://remacle.org/bloodwolf/erudits/strabon/livre173.htm
The historian Pomponius the Milli from the first century AD reminds us that the Moulouya River is the difference between the Kingdom of Numidia in the Central Maghreb and the Kingdom of Mauritania Tangiers, which now represents the Far Maghreb.
The geographer and historian Ptolemy, the most famous geographer from that era, stated that the Moulouya River was taken as a dividing line between Tangier Mauritania and Caesarea Mauritania
"The mauve river separates the two Mauretanias"
See the book of Ptolemy's geography translated into Arabic by Muhammad Al-Mabrouk Al-Duwaib at the following link
https://www.noor-book.com/%D9%83%D8%D9%88%D8%B3-pdf
It is historically documented that the Kingdom of Numid, especially the reign of Jugurtha, extended as far as the Moulouya River in the Far Maghreb today
Moulouya (Berber: melouit; rural pronunciation: meloushet) is a river in northeastern Morocco .
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/81/Moulouya.png/560px-Moulouya.png
The historian Polybus the Milli says around 42 AD that Numidia extends from the Moulouya River to the east towards Tunis and its capital is Cirta.
POMPONIUS MELA
LAND DESCRIPTION
BOOK I
http://remacle.org/bloodwolf/erudits/mela/livre1.htm
POMPONIUS MELA
As for the Mulucha, of which I have spoken, it is a river which, after having formerly served as the limit of the kingdoms of Bocchus and Jugurtha, no longer distinguishes today except the nations which they had under their power .
VI. Numidia.
Numidia extends from the shores of the Mulucha to those of the Ampsaque ; it is smaller than Mauritania, but more cultivated and richer. Its most considerable towns are Cirta, far enough from the sea,
The Moulouya River, which is currently located in the state or kingdom of the Far Maghreb, was always the dividing line with the state of Algeria and the Middle Maghreb. It was mentioned on several occasions and in ancient books that occurred before BC, such as the Greek Carthaginian war, and Hannibal's campaign against the Romans.
The Moulouya River as a dividing line between the Middle Maghreb (Algeria) and the Far Maghreb remained known and agreed upon until the 15th, 16th and 18th centuries AD.
In maps dating back to the Ottoman Navy, the Italian sailor, Piri Rice, in his name is Kitab al-Bahriah, compiled in Turkish, written in 1521 AD.
And his book on marine science and the industries of navigators, in which there are 31 maps of maps that describe coasts, islands, castles, ports, and others. Transferred to Arabic Muhammad Harb.
We find in the map a description of the countries of the Maghreb Al-Ask that it is the Kingdom of Algeria
Its borders are the Moulouya River
Link to see the map of Kitab-i Bahriye "Pirî Reis Photo No. 541 showing the Moulouya River, the boundary between the Algerian Kingdom of Tlemcen and the Kingdom of Fez in Morocco
https://www.loc.gov/resource/gdcwdl.wdl_09210/?sp=541&st=image
The picture on page 543 of the previous reference shows the description of Algeria in the Middle Maghreb
https://www.loc.gov/resource/gdcwdl.wdl_09210/?sp=543&st=image&r=0.071,0.387,0.3,0.733,270
In the book of the Danish historian George Host, a book titled The Kingdom of Marash and Fez, it is mentioned on page 85 that the Moulouya River is the separator between the Kingdom of Marrakesh and the Kingdom of Tlemcen, which he said belongs to Algeria.
Georg Höst, Intelligence on Marokos and Fes,
Relations on the kingdoms of Marrakech and Fez collected in these countries from 1760 to 1768
Direct link to download the book
https://ia800204.us.archive.org/17/items/HoestEfterretninger1779/Hoest-Efterretninger-1779.pdf
second link
https://archive.org/details/HoestEfterretninger1779/page/n7/mode/1up
In the same book, we find a map showing the borders of the Kingdom of Fez and Marrakesh with the Kingdom of Tlemcen, which belongs to Algeria, in the neighborhood of Nara. It is clear that the Tlemcen region extends to the end of the Moulouya River.
The Moulouya River remained the boundary between what is known as the Far Maghreb and the Middle Maghreb until the French occupation of Algeria. The French historian and ambassador in the Kingdom of Marrakesh, Louis de Chenier in 1790 AD, reminds us about 40 years before the French occupation in his book Historical Research on the Moors and the Kingdom of Marrakesh, page 17 The Moulouya River is the last border of the Kingdom of Marrakesh from the east with Algeria
historical research on the moors and history of the empire of morocco
book link
https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k861904.image
Page link directly
https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k861904/f23.item
After the French occupation of Algeria came the “La La Maghina” agreement in 1845, between the Kingdom of Marrakesh and France, according to which France ceded an entire border strip of Algeria’s soil that includes ancient Algerian cities such as Oujda and Guercif, as a bribe from the French to the Alawi Moroccan Sultan in order to prevent support for the Prince Abdul Qadir and his revolution, and thus, a cut took place from the middle soil of Morocco, which is Algeria, and the current political borders were created
Starting from the date of 1845 AD, we see in the French and European references that the border between the Al Aqsa Maghreb region and Algeria is the Tarra Mountains, which are located in the Tlemcen region, which is the well-known border to the present time.
Source: The Struggle of the Amazigh Nation
https://amazighrevolutions.blogspot.com/2019/05/02.html