On Mars, this crater looks like a dinosaur footprint or a legendary bird
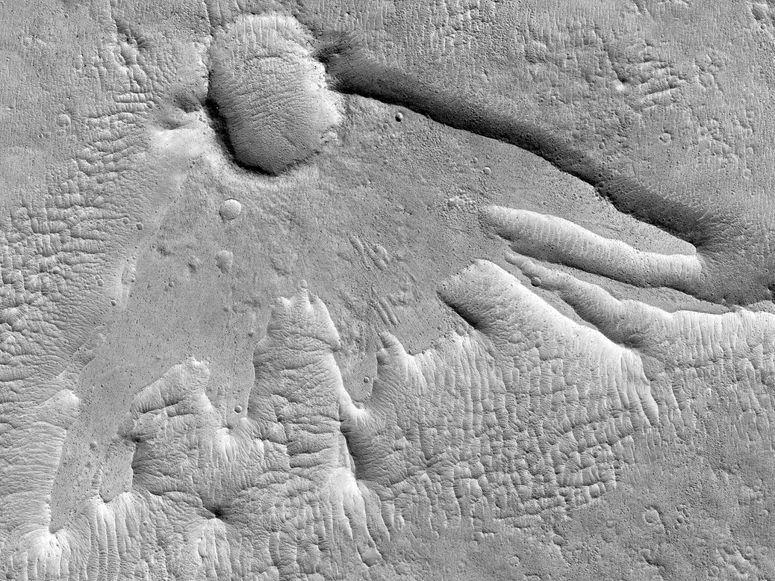

Not all impact craters have a circular shape. The surface of Mars is proof of this. The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft actually captured a crater that looks like a legendary bird or dinosaur footprint.
Impact craters trace the history of our solar system. They allow us to determine the chronology of spatial events. The older a celestial body, the higher the density of craters on its surface. Did you know that 80% of the Moon's surface is covered in craters? The Earth has also not been spared by meteorites in the previous 4 billion years. The impacts of meteorites on Earth are also at the origin of the formation of complex diamonds with astonishing properties . On Mars, the situation is identical. The surface of the red planet is indeed littered with more or less large craters with more or less amazing shapes.

While awaiting the habitats of the first solar-powered astronauts , Mars hosts several rovers on its surface like NASA's Perseverance which finds traces of the ancient presence of liquid water . From space, probes constantly scan the surface of the red planet in an attempt to unlock the secrets of its history. This is how the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) space probe discovered a crater unique in its shape.
An asteroid or comet hit Mars at a low angle to create this peculiar shape
This crater nicknamed "Martian thunderbird" was photographed in the southern hemisphere of Mars by the probe's HiRISE camera. With a resolution of 30 centimeters per pixel and a weight of 65 kg, HiRISE is the most powerful camera ever sent into the solar system. She has been studying the many impact craters on Mars for several years now. Instead of being circular in shape as is often the case, this crater is reminiscent of a dinosaur footprint or a thunderbird, a gigantic legendary bird in Native American culture.
As NASA explains, the shape of this crater is due to an oblique collision. That is, the asteroid or comet responsible hit Mars at a low angle. At the moment of impact, the majority of the debris was ejected towards the top of the image where we can see a raised plateau. The scattering of the rest of the debris created this interesting shape on the ground. On Earth, the best example of oblique impact that we know of is the famous Chicxulub crater in Mexico which was one of the causes of the mass extinction of the dinosaurs.
This 5 km crater is tiny compared to the impact basins of several thousand km on Mars
The crater is 5 km long. Although it may seem giant to us, Mars is home to hundreds of thousands of craters of this size. It is even rather tiny compared to the nearby Schiaparelli crater which is 471 km in diameter. The Hellas Planitia impact basin is even more gigantic with its 2,200 km in diameter.

The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter probe has been studying the red planet since 2006. It has had countless opportunities to document a multitude of different craters. Some look like bear heads, others are reminiscent of dinosaur footprints… We also discovered double craters, craters filled with dunes, craters shaped by ice, etc. The relief of Mars is very varied. It must be said that the planet is near the main asteroid belt. It was therefore repeatedly struck by a wide variety of celestial objects at different angles and speeds.
Source : HiRISE Operations Center

