? How do astronomers measure the vast distances between stars

the light
Light was - and still is - our guide everywhere on Earth, and even in the deep space of the universe, whether this light was the result of stellar radiation, interactions and explosions, or sunlight reflected on moons and objects where it was able to illuminate them. Through the properties of light, we were able to create a more accurate picture of our cosmic world. Starting with Galileo about 400 years ago, he observed the stars of the Orion constellation in 1610 when he directed his telescope at Jupiter.
The light also provided us with a more accurate picture of the nature of the universe when Edwin Hubble explained that the universe is in a state of divergence and expansion by observing the characteristic red spectrum of long waves, issued by distant galaxies, and getting redder the further away they are.
Since light reaches us and explains the universe to us; Astronomers went to study it extensively and find out what it is and its characteristics. The most important of which is knowing its speed, which is about 299,792.5 km/s. Thus, light became a major means of measuring distances in the universe.
Distances in the universe
Determining the distances between celestial bodies in the universe is considered a basic and important means of studying them, as its importance lies in determining the total energy emitted by those bodies, determining their masses and sizes in their orbits, and determining the true movement of stars in space.
Distances in the universe are measured in different length units, and he was the first astronomer to measure the distance between the Earth and the Sun. He is the Greek astronomer “Aristarchus” about 250 years BC.
In the year 1653; Astronomer Christian Huygens measured the distance from the Earth to the Sun and observed the different phases of Venus to determine the angle of the planet's presence in a triangle (Sun, Earth, Venus).
Light year
A common unit of length used to measure very far distances in the universe. A light year is defined as the amount of time it takes light to travel a distance through space during one Earth year, or 365.25 Earth days.
The first person to use the term light year to measure distances in space was the German scientist Friedrich Bessel in 1838. He was able to measure the distance between Earth and the star Cygni 61, and found that the star is located at a distance equal to Earth's orbital radius about 660,000 times.
In 1851; The term "light year" became popular in Germany as "Lichtjare", and was eventually adopted as "light year" officially to describe the vast distances in the universe. Light-years can be divided into light-days, light-hours, or even light-seconds, and these units are sometimes used.
We can say that the sun is located 8 light minutes away; This means that light takes about 8 minutes to reach Earth from the Sun.
Astronomical unit – AU

An illustration of the astronomical unit AU, which represents the distance between the Earth and the Sun from half of Earth's orbit.
Distances between the Sun and the planets are also measured in a unit of length called the “Astronomical Unit” or AU for short, which is equal to the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. That is, it is calculated from the radius of the Earth's orbit around the sun, not the entire orbit, which is why this astronomical unit is equal to a value estimated at about 150 million km.
Triangle system – Parallax
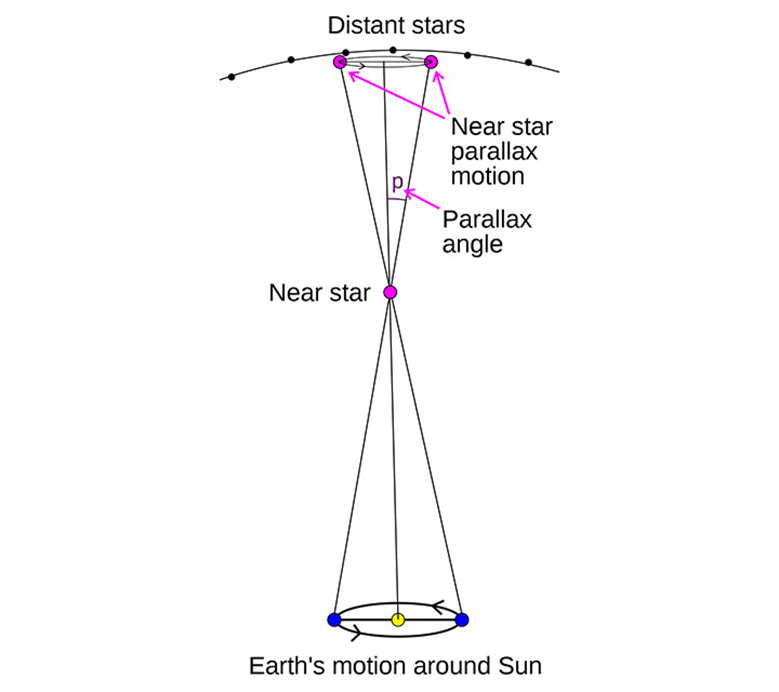
The trigonometric system for studying the change in the position of a star relative to a person observing it on Earth during a year from the east and west.
Astronomers rely on the “parallax triangular system” in general to measure the vast distances between celestial bodies and the Earth and the sun, where the Earth, the sun, or any celestial body forms a celestial triangle in which the angle of incidence of light emanating from the celestial body is determined. Which reaches the ground.
Giovanni Cassini used a theory based on this system in 1672 to determine the distance from the Sun to Mars. And for this reason; He sent his colleague Jean Riker to the French Guiana region while he was staying in Paris. His theory was to determine the position of Mars relative to the stars behind it, and to project those measurements to the known distance between Paris and Guyana.
The triangular system depends on observing the apparent movement of nearby stars with respect to groups of stars far away from them. This movement results from a change in the position of the observer as a result of the Earth’s rotation around the Sun and the change in its position in orbit during the year.
If you are in January, for example; You will observe a nearby star in the sky towards the east, and six months later in December; You will find it on the western side. The change in a star's position is caused by the Earth's position in orbit, and astronomers note this difference to calculate distances between stars.
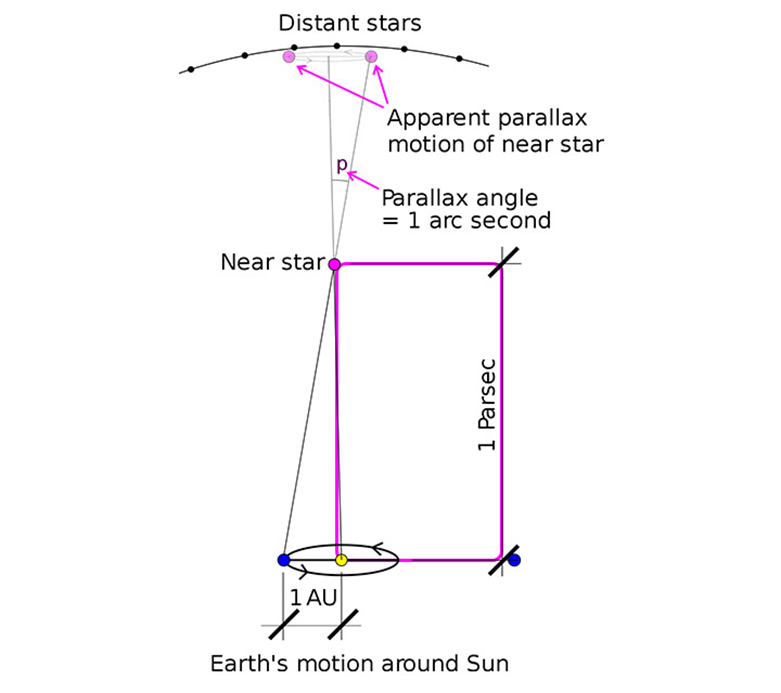
Illustration of the parsec unit that measures the vast distances in the universe.
“Parsecs” is also a unit of length to measure the huge distances between stars and galaxies in the universe, as a parsec equals about 30 trillion (a thousand million) km, or 3.26 light years. If we measure the distance between the Earth and the Sun, for example; We will find it to be 0.000004848 leagues.
The center of our galaxy is located more than 8,000 parsecs away in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. As for the Andromeda Galaxy, which is considered the closest galaxy to us; It is approximately 800 kilometers away from us. On a larger scale; Astronomers study giant structures of majestic proportions in the universe such as clusters, or a group of thousands of galaxies close to us, which would be about 54 million years away if we decided to travel towards them at the speed of light. These dimensions and structures can be measured in units derived from parsecs, such as the mega, which is equal to about a million parsecs, or the giga, which is equal to a billion parsecs!
As for the relationship of the parsakh to the triangular system - parallax; Continuing the previous example of observing a star during a year, we will find that we are observing the star in two different locations 300 km apart. If the star is close, its movement will be clearly visible. Astronomers can calculate the parallax angle (α), which is the angle that arises in the triangle made by the observing path between the Earth, the stars or the observed object, and the Sun.
Finally, the universe gives us small clues to tell us about the secrets it hides by which we can realize the truth of our existence in it. Determining distances are the most important keys that give us a closer picture of space, and to understand the size and presence of other planets around us.
Source: websites

