The world faster than light.. the search for a speed that transcends time and space

Perhaps, during the past 100 years, no man in the world gained fame and media momentum as Albert Einstein, the owner of the messy hairdo and the old smoking pipe, and no one knew whether the greatest discoveries of modern science were being led to him or whether he was the one who was seeking it, whether Realized or not.
It is the summer sun of 1902 that cast its warm rays on the Swiss streets of Berne; The place that this young scientist longed for and aspired to work as a technical expert in the Federal Office for Intellectual Property, which is called in slang "the Patent Office".
By 1905, Einstein obtained a doctorate from the University of Zurich, coinciding with obtaining Swiss citizenship, but this was not the greatest that he experienced in that year, which historians refer to as the year of the miracle (Annus Mirabilis).
Einstein would not have had these scientific researches go through without scrutiny and examination. The fruit of his extensive and extensive knowledge was the publication of 5 research papers, the most famous of which was his famous theory of “special relativity” that changed our view of the universe forever.
The most famous equation formulated by Einstein within his special theory of relativity, which states that the product of mass multiplied by the square of the speed of light is equal to its energy, which is known as the principle of mass-energy equivalence; The coefficient of the speed of light represents the cornerstone of the law, assuming that the universe has a maximum speed, which is the speed of light, and any exceeding of this speed will lead to the collapse of the universe on itself, or in other words the collapse of those laws that describe the mechanism of the universe’s work.
Quantum estimation.. the first calculation of the speed of light
Einstein was not the first man to calculate the speed of light. He was preceded by decades of various attempts by various scientists, the first of which was the Danish astronomer “Ole Römer” in the 17th century, who was working at the Paris Astronomical Observatory while working to collect observations on Io, the fourth largest moon. Big Jupiter. Romer noticed that when the Earth is at its closest point with Jupiter, an eclipse of Io occurs about 11 minutes earlier than expected based on the average orbital period over many years of observation, and at the farthest point from Jupiter - that is, after 6 and a half months - an eclipse occurs Another one for the same moon, but it happens 11 minutes later than expected.
Of course, it was not at all obvious to know the reason for the occurrence of this time difference, given that the classical Newtonian rules forbade dealing with light as anything other than being instantaneous. The old belief was that light was too fast to be measured, or that its speed was infinite. And it cannot be dropped under any measurement methodology.
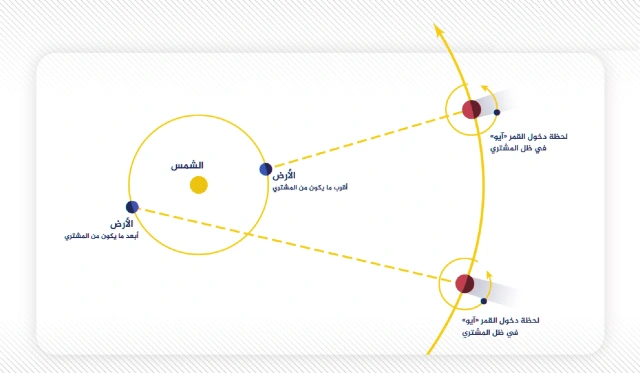
While observing the movement of one of Jupiter's moons, Romer noticed that its rotation period varies every six months, which led him to estimate the speed of light.
It may have taken some time to overcome these postulates, but Romer's experiment opened a door to the question: Why did this time difference occur between the dates of the two eclipses when the Earth's position with Jupiter changed? The answer, of course, is: because light has a finite speed and it takes time to travel a distance between any two points.
And if the speed of light actually has a limit, what is this limit? This prompted the Dutch mathematician "Christian Huygens" to investigate the matter in the course of his astronomical calculations. These calculations resulted in a speed of 210,000 kilometers per second, which is 30% less than the true speed of light. The reason for the poor result was Huygens' reliance on inaccurate observational numbers for the timing of the eclipse, as well as his inaccurate knowledge of the dimensions of the planets' orbits, but it was the first answer that gives a quantitative estimate of the speed of light.1
Electromagnetic theory.. Four laws of the relationship between electricity and magnets
With the development of measuring instruments over the following decades, the accuracy increased and the results approached the correct number for the speed of light, but the decisive moment came only at the hands of the Scottish mathematician “James Maxwell” in the mid-19th century, he created the theory of electromagnetism and formulated his famous four laws to explain the relationship between the two forces Electricity and magnetism.
Maxwell discovered that a change in the electric field would create a magnetic field, and vice versa. This means that electric waves are able to produce magnetic waves, which in turn produce electric waves to return to produce magnetic waves again, and the loop continues in this way.
Physically, both types of waves can be depicted as perpendicular to each other, so that the angle between the path of the electric wave and the path of the magnetic wave is 90 degrees, and in this way these waves are able to travel and move in space and everywhere.

Spacetime, the fabric of the universe that bulges more around the most massive objects, is another concept of gravity
When Maxwell wanted to calculate the speed of these combined electromagnetic waves, he found that the numbers are very similar to those that scientists found before him when calculating the speed of light. And it seemed more exciting now, so he concluded that the light may be in its essence electromagnetic waves only.2
When Einstein was introduced later at the beginning of the twentieth century, he was not concerned at all with the speed of light, but was rather involved in depicting the universe in a more coherent physical framework than it is in classical physics. Einstein realized the true relationship between time and space, which represent the cosmic fabric, defining them with a term combined with "space-time", and here a problem appeared on the horizon!
We have always realized that time is different from space in its mathematical origin, for space is a unit of measurement in meters or feet, while time is its second unit of measurement, and these two units are completely different from each other. So now he had to find a link and a relationship to translate the movement between space and time, in other words; What does one meter of space correspond to in time, and what is the necessary “transformation rate” between them?
This is what prompted him to search in the old equations for this strange equation, and he did not stay long until he found what he wanted after applying his special relativity to Maxwell's equations, and he found that this equation equals the speed of light in a vacuum completely, which is 300 thousand kilometers per second. Here it became clear to him that the finite picture of the cosmic fabric is bound by a quantity equal to the speed of light, and nothing can exceed this quantity with its speed.
The top speed barrier... Do we have to believe it?
His condition is like the case of those who glorified before him, the eyes are waiting for him for any slip and error, and this situation has continued from yesterday to today, knowing that everyone who knew Einstein realized that the man is difficult to reach, and his renewed old victories still amaze the scientific community to this moment, but this did not It prevents some from reconsidering some critical issues, the first of which is the limit of the maximum speed of the universe.
In fact, Einstein was not interested in knowing the importance of the speed of light for himself, and he was not concerned with that in the first place, but the coincidence of the numbers that resulted from the calculations is what led him to say that the value of the "transformation rate" - which we mentioned earlier - is equal to the value of the speed of light, and therefore it is Nothing can move and move beyond this speed and value.
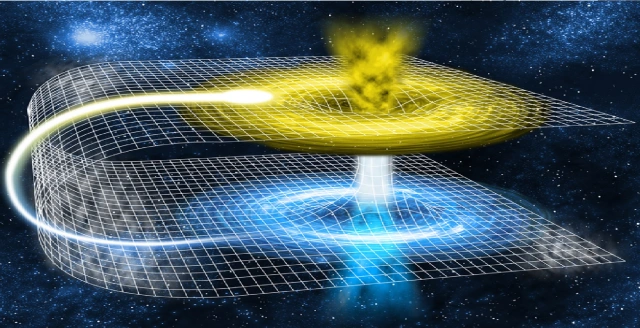
The worm tunnel, a hypothesis put forward by cosmologists to travel through time faster than light
Scientists point out that light is able to achieve this value because it consists of massless elementary particles called photons, and any other body or particle with a mass is impossible for it to achieve this speed, and in the best possibilities it can only be approached.
These may be just calculations that agree with data that were previously assumed based on some facts, but if the data change, will the results change? So some ask. Therefore, what prevents the proving or disapproval of Einstein's theories is theoretical or practical experience. Here we review the most prominent "theoretically" proposals in this regard over the past few decades.
"Warp Engine"...the way of spaceships
In a research paper presented by the Mexican physicist "Miguel Alcubierre" in 1994 entitled "Warp Engine.. Ultra-fast Travel within General Relativity", in which he proposed a methodology different from the traditional pattern of traveling and navigating in deep space at high speeds, without violating any of the physical rules of the universe. In his introduction, Alcubierre says, “It is well known that within the framework of general relativity it is possible to distort the fabric of space-time in such a way as to allow a spaceship to travel very quickly.”3
This distortion is caused by a wave that creates a contraction in space in front of it and expands behind it, and then the spacecraft will enter inside this wave, which is known as the warp bubble, and this bubble will explode at high speeds without the spacecraft having to move.
This space-time bubble can travel in space at speeds far exceeding the speed of light, and the spacecraft's travel will be implicit within it.
Alcubierre likens this process to the post-cosmic era and the process of its expansion, as the universe is expanding at speeds greater than the speed of light. If there were two observers in a space within this expansion, it would be easy to say that these observers are traveling at a speed greater than the speed of light, but this is not true, because they are still within the cosmic boundaries that prevent this, and what we see is a violation of the speed of light is the speed of the expansion of the universe same.4
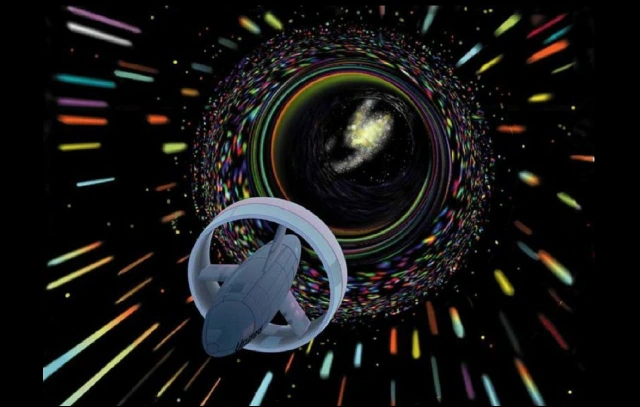

The Warp Engine creates a bubble distortion in space-time as it travels around the universe
In order to achieve such a model we need to understand the "Casimir effect", in short, a physical force that occurs on a microscopic scale in a very narrow space. It seems to be a complicated definition, but an example can be given that is easy to understand. If we place two opposite uncharged plates separated by a very limited distance - perhaps a few micrometers - in the vacuum, then there is a limited attractive force that results from these plates.
Scientists believe that using this force would enhance the idea of creating a warp drive by pulling the spacecraft forward by shrinking spacetime itself.
On the practical level, a team of scientists led by Dr. Harold White, a physicist and engineer at NASA, has proposed a structure for warp drives that can be created in the real world and used to explore the Casimir effect. This appears to be a small step, but it is a great and possible step, as he described it, and it may open up future horizons for us to implement what the physicist "Alcobierre" published for space travel.6
Strange matter and wormholes...Transportation through time and space
Worm tunnels are nothing but a set of solutions and outputs from Einstein’s equations for the general theory of relativity, a joint discovery between Einstein himself and the American physicist “Nathan Rosen” in 1935. They extracted a “theoretical” model of astronomical bridges connecting two points separated by great distances in space-time. They called them "Einstein-Rosen bridges" before the name was later changed to tunnels or wormholes
Theoretical physicists believe that this means of transportation is capable of directing any object to very distant points at speeds exceeding the speed of light, provided that the movement is not within the local reference frame, that is, that the movement be within the space-time fabric, which is what these wormholes provide exactly as a method of "engine" distortion", which was mentioned above.
In the origin of their existence, they are like black holes, where mathematical deductions were the first evidence of their existence, although black holes were followed by direct monitoring by high-tech radio telescopes and documented during the past two years, and this has not happened with wormholes until this moment. .
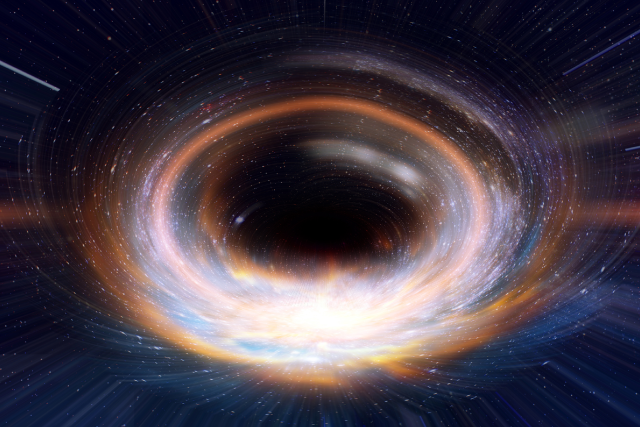

A black hole, one of the two wormholes to the other side of the universe
Many - including the wormhole theory theorists themselves - believe that such cosmic bridges are not possible, in addition to being very dangerous because they are unstable, meaning that they collapse suddenly and decay without prior notice.
In describing the wormhole, it has two orifices, one of which is a black hole and the other a white hole, and this is despite the fact that white holes have not been discovered until this moment, but the other is from the deductions of the theory of relativity presented by the Austrian physicist "Ludwig Flam".
These two craters or entrances connect two distant points in the universe by a bridge lined with "strange matter", and the effect of this substance works in opposite to the effect of natural materials because it contains negative energy density and great negative pressure. Instead of attracting things towards it, it makes them repel, and the reason for its necessity is that it keeps the wormhole open and extended without collapsing and contracting on itself.
Effect succession.. quantum entanglement and instantaneous transition
When we talk about traveling faster than the speed of light, we cannot overlook quantum physics - or quantum mechanics as it is called - in this tiny world where the logic of laws differs and the calculations differ. The theory of quantum entanglement is one of those strange and exciting phenomena that occupy a great place among quantum physicists.
This theory assumes two bodies at the level of the quantum world, that is, very small, with a quantum relationship between them with speed, position, momentum, spin and other properties, and they are affected by the same effect. One pair to know the properties of the other, which is why it is called quantum entanglement.
This branch of physics is concerned with the subatomic world. And because its application is very difficult, its hypotheses are often adopted theoretically and mathematically without resorting to direct application due to the lack of the machine and the means. In a 1935 research paper, Einstein, Rosen and Russian physicist Boris Podolsky presented a study of how strongly quantum states are related to each other, and found that when two particles are closely related, they lose their individual quantum state and instead share a single unified state.
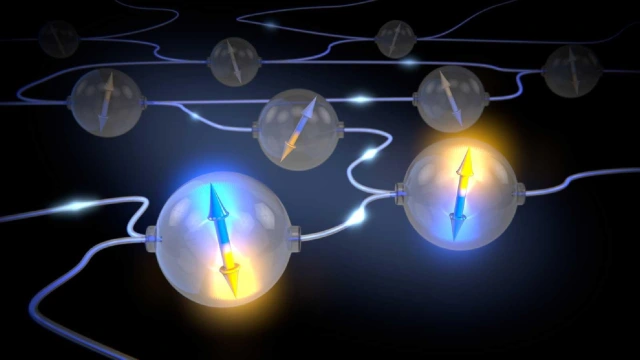
Quantum entanglement is a relationship between two objects in the quantum world with velocity, position, momentum, and spin
Also, the distance factor is not important in this theory, that is, no matter how much it is, the results will be the same. The German scientist Erwin Schrödinger - one of the founders of quantum physics - believes that quantum entanglement is the most fundamental axes in the quantum world, and that the existence of such a theory is a complete departure from the classical methodology of thinking.
As long as the transmission and the effect are instantaneous, then it is imperative that the information sent between two points travel at a speed higher than the speed of light, and in this way we will break one of the main rules of the universe. It is not that simple, and Einstein previously referred to this dilemma, describing it as "terrible work from a distance."
Although there is no clear solution to this dilemma yet, it can be said: Just as quantum entanglement adopts the property of instantaneous transmission, it also preserves the principle of causation, meaning that nothing happens without a cause.
If an observer of a quantum body follows its state, he will not realize the effect on it until he obtains information to compare that effect from the sending observer, and this information will not arrive until after the distance travels at a speed not exceeding the speed of light. Therefore, many believe that such a method is still locked in the speed of light, despite its apparent instantaneous communication.
Tachyons..Ultra-Flexible Particles
In 1967, an American physicist from Columbia University, Gerald Feinberg, published a research paper entitled "The Possibility of Existing Particles Faster Than Light", reviewing imaginary particles that have different properties and using the special theory of relativity, which is the first time that the term "tachyon" appears. In Greek, it means a very small and agile particle.
Feinberg hypothesized that there are two types of subatomic particles, one of which is the paradiodes, which represent everything related to the mass of the visible world.
As for the other type, tachyons differ from their counterparts in that they lose energy instead of gaining it when their speed increases, and for this reason they can theoretically cross the speed of light, but rather they should always be in this range of speed and below.

Tachyons are particles that lose energy as their speed increases, which theoretically allows them to pass the speed of light
When talking about tachyons or tectonic particles, some may imagine that they are a kind of fantasy or that it is one of the fancies of science fiction writers in their quest to create novel excitement, but the matter has scientific dimensions much further than that, as tachyons theoretically do not violate the laws of relativity what As long as it adheres to the condition of an infinite increase in energy with an increase in speed.
But what actually contradicts the existence of tachyons is that they contradict in essence one of the physical principles, which is the causation that we touched upon earlier, because of course they are able to break the space-time constant that links the cosmic fabric, that is, the value of the speed of light, and therefore able to travel in time to the past, and automatically we will find We are faced with the famous "grandfather paradox".
In conclusion, the threshold of the speed of light is still a difficult dream for physicists who dream of breaking the fork of Einstein’s theory of relativity, and perhaps it is the ambition that astronauts target for those who want to reach the ends of the universe and its edges from one galaxy to another, given what its limited age allows.
Working under the umbrella of the principles of general relativity will not allow the existence of any particles that penetrate the cosmological constant of the speed of light in a vacuum, and the only solution is to circumvent these equations. Instead of the reference frame being local, it will be on a larger scale, i.e. in the cosmic fabric itself by causing a distortion in it, as wormholes do as well as the Alcubierre actuator, and then space-time will give us the opportunity to move at speeds exceeding the speed of light many times, just as is happening now in the expansion of the universe that Exceeds the speed of light.
Sources:
[1] Editors of the site (date unknown). Ole Romer and the speed of light. Retrieved from: https://www.amnh.org/learn-teach/curriculum-collections/cosmic-horizons-book/ole-roemer-speed-of-light
[2] Sitter, Powell (2020). Why is the speed of light the same? Retrieved from: https://www.space.com/speed-of-light-properties-explained.html
[3] Alcubierre, Miguel (2000). Research paper: Torsion Engine: Ultrafast Travel within General Relativity. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Wales.
[4] Same source.
[5] Hall, Jessica (2021). Scientists haven't "made" a bubble warp, but they're closer to testing one. Retrieved from: https://www.extremetech.com/extreme/329631-scientists-havent-created-a-warp-bubble-but-theyre-a-bit-closer-to-testing-one
[6] Clark, Aubrey (2022). Did we find the warp drive? Scientists explain how this happens. Retrieved from: https://www.sciencetimes.com/articles/35310/20220101/warp-bubble-found-scientists-explain-how-this-works.htm
[7] Tillman, Nola (2022). What is the wormhole theory? Retrieved from: https://www.space.com/20881-wormholes.html
[8] Starr, Powell (2021). What is quantum entanglement? Retrieved from: https://www.livescience.com/what-is-quantum-entanglement.html
[9] Editors of the site (date unknown). Is quantum communication faster than the speed of light? Retrieved from: https://quantumxc.com/blog/is-quantum-communication-faster-than-the-speed-of-light/#:~:text=No%20real%20information%20is%20passed%20when% 20the%20entangled%20particles%20affect%20each%20other.&text=The%20end%20result%20is%20always,than%20the%20speed%20of%20light.%E2%80%9D
[10] Lee, Robert (2021). Tachyons: Facts About These Faster Than Light Particles. Retrieved from: https://www.space.com/tachyons-facts-about-particles
https://doc.aljazeera.net/%D8%AA%D9%82%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%8A%D8%B1/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A3%D8%B3%D8%B1%D8%B9-%D9%85%D9%86-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B6%D9%88%D8%A1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%AB-%D8%B9%D9%86-%D8%B3%D8%B1%D8%B9%D8%A9-%D8%AA/?fbclid=IwAR2r-Lm-9aXF2yvUBZ5ihgTgBZilEL9dSplD-Mg1BXy2rT4fko7GpUF8CMA

